Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A85397-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A85397-01 |
|
SQL Statements:
DROP SEQUENCE to UPDATE, 24 of 27
Use the SET TRANSACTION statement to establish the current transaction as read only or read write, establish its isolation level, or assign it to a specified rollback segment.
The operations performed by a SET TRANSACTION statement affect only your current transaction, not other users or other transactions. Your transaction ends whenever you issue a COMMIT or ROLLBACK statement. Oracle implicitly commits the current transaction before and after executing a data definition language (DDL) statement.
If you use a SET TRANSACTION statement, it must be the first statement in your transaction. However, a transaction need not have a SET TRANSACTION statement.
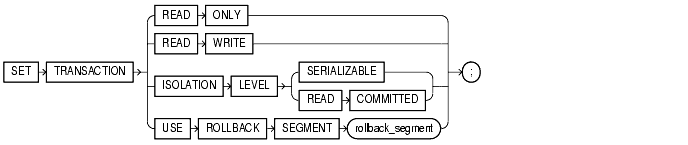
READ ONLY
The READ ONLY clause establishes the current transaction as a read-only transaction. This clause established transaction-level read consistency.
All subsequent queries in that transaction only see changes committed before the transaction began. Read-only transactions are useful for reports that run multiple queries against one or more tables while other users update these same tables.
Restriction: Only the following statements are permitted in a read-only transaction:
SELECT statements without the for_update_clause)
LOCK TABLE
SET ROLE
ALTER SESSION
ALTER SYSTEM
READ WRITE
Specify READ WRITE to establish the current transaction as a read-write transaction. This clause establishes statement-level read consistency, which is the default.
Restriction: You cannot toggle between transaction-level and statement-level read consistency in the same transaction.
ISOLATION LEVEL
Use the ISOLATION LEVEL clause to specify how transactions containing database modifications are handled.
USE ROLLBACK SEGMENT
Specify USE ROLLBACK SEGMENT to assign the current transaction to the specified rollback segment. This clause also implicitly establishes the transaction as a read-write transaction.
This clause lets you to assign transactions of different types to rollback segments of different sizes. For example:
You cannot use the READ ONLY clause and the USE ROLLBACK SEGMENT clause in a single SET TRANSACTION statement or in different statements in the same transaction. Read-only transactions do not generate rollback information and therefore are not assigned rollback segments.
The following statements could be run at midnight of the last day of every month to count how many ships and containers the company owns. This report would not be affected by any other user who might be adding or removing ships and/or containers.
COMMIT; SET TRANSACTION READ ONLY; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM ship; SELECT COUNT(*) FROM container; COMMIT;
The first COMMIT statement ensures that SET TRANSACTION is the first statement in the transaction. The last COMMIT statement does not actually make permanent any changes to the database. It simply ends the read-only transaction.
The following statement assigns your current transaction to the rollback segment oltp_5:
SET TRANSACTION USE ROLLBACK SEGMENT oltp_5;
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|