|
|
Akt Signaling Pathway
The Akt pathway is another important
pathway due to its role in apoptosis. Upon binding by growth
factors, the cell surface receptors will act as scaffolds in their
intracellular domains for specific binding interactions between
cytosolic proteins. This leads to the activation of Phosphoinositide
3-Kinase (PI3K), which will catalyze the phosphorylation of
Phosphotidylinositol 4,5-biphosphate at the inositol ring, forming
PIP3. PIP3 will then recruit proteins
containing the Pleckstrin homology domains, which includes the
protein Akt. At the membrane, it is then able to interact with
PDK1
and becomes phosphorylated. Phosphorylated Akt is then released into
the cytosol where it will phosphorylated Bad at its Ser136
residue.
Bcl-2 Protein Family
The Bcl-2 family of
proteins regulates programmed cell-death (apoptosis). It comprises
of anti-apoptotic members (Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL) and pro-apoptotic
members (such as Bax and Bad). Bcl-2 and Bcl-xL inhibit the release
of cytochrome c from the mitochondria. This release will lead to the
activation of procaspase 9, a protein that is directly involved in
cell death. Bcl-2 inhibits the release by binding to the
pro-apoptotic Bax, preventing it from forming pores in the
mitochondria.
On the other hand,
phosphorylated Bad can bind competitively to Bcl-2, such that cytosolic
Bax will be able to translocate to the mitochondrial
membrane, causing cytochrome c to be released into the cytosol. The
Akt pathway hence regulates apoptosis by phosphorylating Bad.
Modeling the Akt
Pathway
The Akt pathway
does not operate in isolation. Its activity affects or is being
affected by other pathways, one of them being the Extracellular
Regulated Kinase (ERK) signaling cascade. Besides down-regulating
ERK activation by Akt-dependent Raf phosphorylation,
PDK1 (one of
the components of the Akt pathway) can also regulate the ERK pathway
in a MEK (MAPK/ERK Kinase) dependent manner. With this in mind, we
came up with a model of the Akt signaling pathway, which also
includes some other possible means of interactions, i.e. via the
Pak-1 Kinase, as well as common downstream targets such as Bad.
|
 |
|
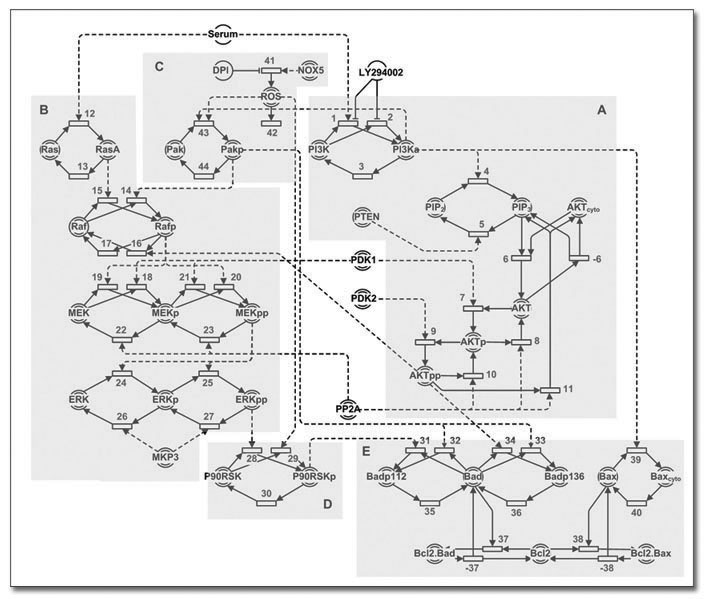
The Hybrid Functional Petri Net model
of the Akt and ERK pathways. (A) is the module showing
the Akt pathway, starting from the activation of PI3K by
Serum. (B) shows the ERK cascade from Ras down to ERK.
(C)-(E) shows the other modules that are related to the
two main pathways, with (C) representing the ROS module,
(D) depicting the RSK module and finally (E), the Bcl-2
family module |
|
 |
|
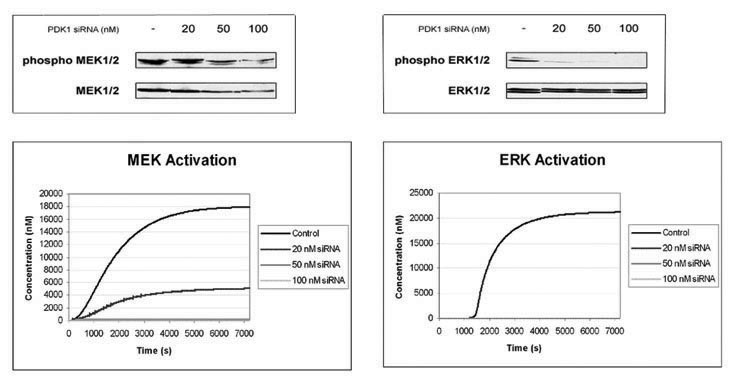
Profiles of MEK and ERK activation
levels compared to experimental data |
Validation and
Parameter Estimation
|
In any modeling
endeavor, the bottleneck is the estimation of the parameters for
the various rate equations. Technical difficulties and huge
resource requirements make the experimental determination of all
the parameters impossible and hence they have to be estimated.
This amounts to a global optimization problem. There are several
techniques to solve such problems, however all of them face the
same problem of high dimensional search space. In modeling the
Akt signaling pathway, we attempted to exploit the network
topology by breaking them down into modules and arranging them
in a Directed Acyclic Graph, such that estimation can be done
module-by-module. |
 |
|
|
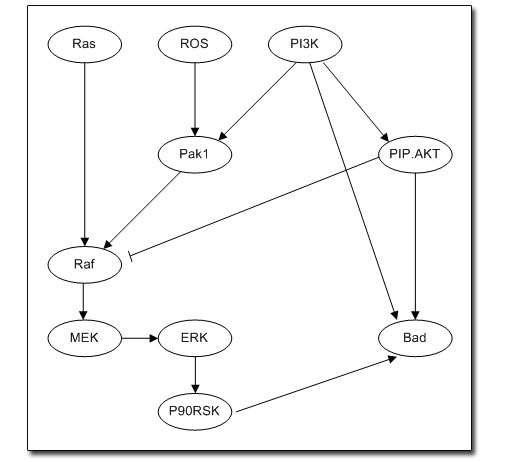
Directed acyclic graph of the
individual modules that make up the pathway |
|
 |
Another issue
that is largely ignored in several models is proper
model validation. Model validation is "the
substantiation that a computerized model within its domain of
applicability possesses a satisfactory range of accuracy,
consistent with the intended application of the model -
Schlesinger '79". Whilst most models based their correctness
on the visual comparison of the concentration of some molecular
species with experimental data, a more objective form of
validation is needed to establish a certain "level of
confidence" in the accuracy of the model and its parameters. |
|
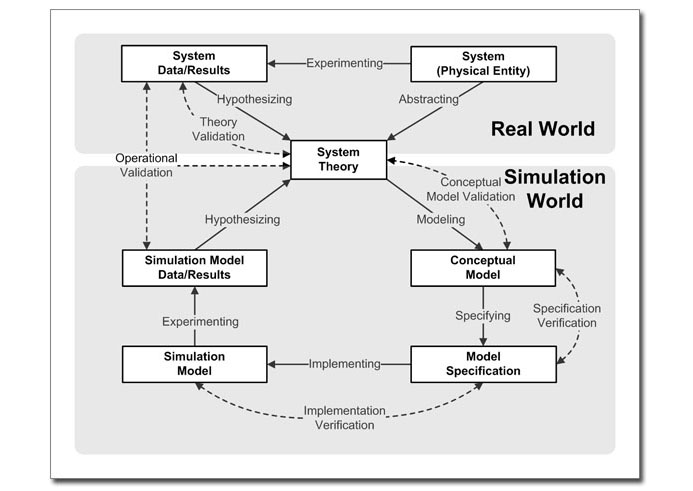
The
validation paradigm as formulated by Robert G. Sargent |
|
|
A comprehensive validation scheme has been proposed by
Robert G. Sargent. But as far as modeling of biopathways
is concerned, our focus is on Operational
Validation, specifically Historical Data
Validation (use of existing experimental data)
and Predictive Validation (use the model
to suggest future experiments and validate with the new
data) to build and assert the correctness of our models.
The formulation of suitable metrics and formal
validation techniques based on available data will be
one of our research goals.
|
[Back]
|
|
|
| |



