Release 2 (8.1.6)
Part Number A76939-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals Release 2 (8.1.6) Part Number A76939-01 |
|
This chapter explains how to enforce the business rules associated with your database and prevent the entry of invalid information into tables by using integrity constraints. Topics include the following:
You can define integrity constraints to enforce business rules on data in your tables. Once an integrity constraint is enabled, all data in the table must conform to the rule that it specifies. If you subsequently issue a SQL statement that modifies data in the table, then Oracle ensures that the resulting data satisfies the integrity constraint. Without integrity constraints, such business rules must be enforced programmatically by your application.
Enforcing rules with integrity constraints is more reliable than enforcing the equivalent rules by issuing SQL statements in your application. The semantics of integrity constraints are very clearly defined, so the internal operations that Oracle performs to enforce them are optimized beneath the level of SQL statements in Oracle. Because your applications use SQL, they cannot achieve this level of optimization.
To ensure that each employee in the EMP_TAB table works for a department that is listed in the DEPT_TAB table, first create a PRIMARY KEY constraint on the DEPTNO column of the DEPT_TAB table with the following statement:
ALTER TABLE Dept_tab ADD PRIMARY KEY (Deptno);
Then create a referential integrity constraint on the DEPTNO column of the EMP_TAB table that references the primary key of the DEPT_TAB table. For example:
ALTER TABLE Emp_tab ADD FOREIGN KEY (Deptno) REFERENCES Dept_tab(Deptno);
If you subsequently add a new employee record to the table, then Oracle automatically ensures that its department number appears in the department table.
To enforce this rule without integrity constraints, you can use a trigger to test each new employee record to ensure that its department number belongs to an existing department. This testing involves issuing a SELECT statement to query the DEPT_TAB table. Because SELECT in Oracle uses "consistent read", the query might miss uncommitted changes from other transactions. Integrity constraints avoid this problem.
In some cases, you might want to enforce business rules through your application as well as through integrity constraints. Enforcing a business rule in your application might provide faster feedback to the user than an integrity constraint. For example, if your application accepts 20 values from the user and then issues an INSERT statement containing these values, then you might want your user to be notified immediately after entering a value that violates a business rule.
Because integrity constraints are enforced only when a SQL statement is issued, an integrity constraint can only notify the user of a bad value after the user has entered all 20 values and the application has issued the INSERT statement. However, you can design your application to verify the integrity of each value as it is entered, and notify the user immediately in the event of a bad value.
All enabled unique and primary keys require indexes, and foreign keys should almost always be indexed. Although unique and primary keys can create unique indexes for you, when you need an index for performance reasons, you should not rely on an index that is automatically created for key columns. Instead, create the index first, by hand.
Note that:
By default, all columns can contain nulls. Only define NOT NULL constraints for columns of a table that absolutely require values at all times.
For example, in the EMP_TAB table, an employee's manager or hire date might be temporarily omitted. Some employees might not have a commission. Therefore, these three columns should not have NOT NULL integrity constraints. However, an employee name might be required in each row, making this column a good candidate for a NOT NULL integrity constraint.
NOT NULL constraints are often combined with other types of integrity constraints to further restrict the values that can exist in specific columns of a table. Use the combination of NOT NULL and UNIQUE key integrity constraints to force the input of values in the UNIQUE key; this combination of data integrity rules eliminates the possibility that any new row's data will ever attempt to conflict with an existing row's data.
Because Oracle indexes do not store keys that are all null, if you want to allow index-only scans of the table or some other operation that requires indexing all rows, put a NOT NULL constraint on at least one indexed column.

Legal default values include any literal, or any expression that does not refer to a sequence, PL/SQL function, column, LEVEL, ROWNUM, or PRIOR. Default values can include the expressions SYSDATE, USER, USERENV, and UID. The datatype of the default literal or expression must match or be convertible to the column datatype.
If you do not explicitly define a default value for a column, the default for the column is implicitly set to NULL.
Only assign default values to columns that contain a typical value. For example, in the DEPT_TAB table, if most departments are located at one site, then the default value for the LOC column can be set to this value (such as NEW YORK).
Defaults are also useful when you use a view to make a subset of a table's columns visible. For example, you might allow users to insert rows into a table through a view. The view is defined to show all columns pertinent to end-user operations; however, the base table might also have a column named INSERTER, not included in the definition of the view, which logs the user that originally inserts each row of the table. The column named INSERTER can record the name of the user that inserts a row by defining the column with the USER function. For example:
. . ., inserter VARCHAR2(30) DEFAULT USER, . . .
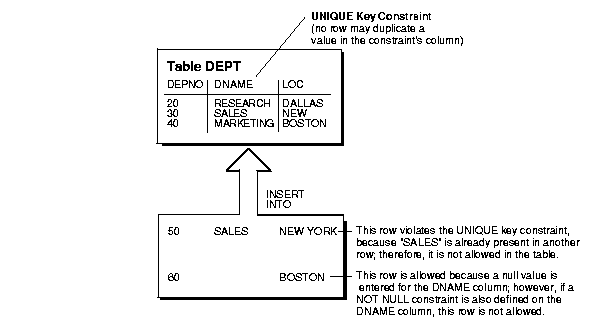
Each table can have one primary key. A primary key allows each row in a table to be uniquely identified and ensures that no duplicate rows exist. Use the following guidelines when selecting a primary key:
The purpose of a table's primary key is to uniquely identify each row of the table. Therefore, the column or set of columns in the primary key must contain unique values for each row.
A primary key value is only used to identify a row in the table; primary key values should never contain any data that is used for any other purpose. Therefore, primary key values should rarely need to be changed.
A PRIMARY KEY constraint, by definition, does not allow the input of any row with a null in any column that is part of the primary key.
Short primary keys are easy to type. You can use sequence numbers to easily generate numeric primary keys.
Although composite primary keys are allowed, they do not satisfy the previous recommendations. For example, composite primary key values are long and cannot be assigned by sequence numbers.
Choose unique keys carefully. In many situations, unique keys are incorrectly comprised of columns that should be part of the table's primary key (see the previous section for more information about primary keys). When deciding whether to use a UNIQUE key constraint, use the rule that a UNIQUE key constraint is only required to prevent the duplication of the key values within the rows of the table. The data in a unique key is such that it cannot be duplicated in the table.
Do not confuse the concept of a unique key with that of a primary key. Primary keys are used to identify each row of the table uniquely. Therefore, unique keys should not have the purpose of identifying rows in the table.
Some examples of good unique keys include
AREA and PHONE (the primary key is the customer number)
Whenever two tables are related by a common column (or set of columns), define a PRIMARY or UNIQUE key constraint on the column in the parent table, and define a FOREIGN KEY constraint on the column in the child table, to maintain the relationship between the two tables.
|
See Also:
Depending on this relationship, you may want to define additional integrity constraints including the foreign key, as listed in the section "Relationships Between Parent and Child Tables". |
Figure 4-3 shows a foreign key defined on the DEPTNO column of the EMP_TAB table. It guarantees that every value in this column must match a value in the primary key of the DEPT_TAB table (the DEPTNO column); therefore, no erroneous department numbers can exist in the DEPTNO column of the EMP_TAB table.
Foreign keys can be comprised of multiple columns. However, a composite foreign key must reference a composite primary or unique key of the exact same structure (the same number of columns and datatypes). Because composite primary and unique keys are limited to 32 columns, a composite foreign key is also limited to 32 columns.
Foreign keys allow key values that are all null, even if there are no matching PRIMARY or UNIQUE keys.
By default (without any NOT NULL or CHECK clauses), and in accordance with the ANSI/ISO standard, the FOREIGN KEY constraint enforces the "match none" rule for composite foreign keys. The "full" and "partial" rules can also be enforced by using CHECK and NOT NULL constraints, as follows:
CHECK constraint that allows only all nulls or all non-nulls in the composite foreign key as follows, assuming a composite key comprised of columns A, B, and C:
CHECK ((A IS NULL AND B IS NULL AND C IS NULL) OR (A IS NOT NULL AND B IS NOT NULL AND C IS NOT NULL))
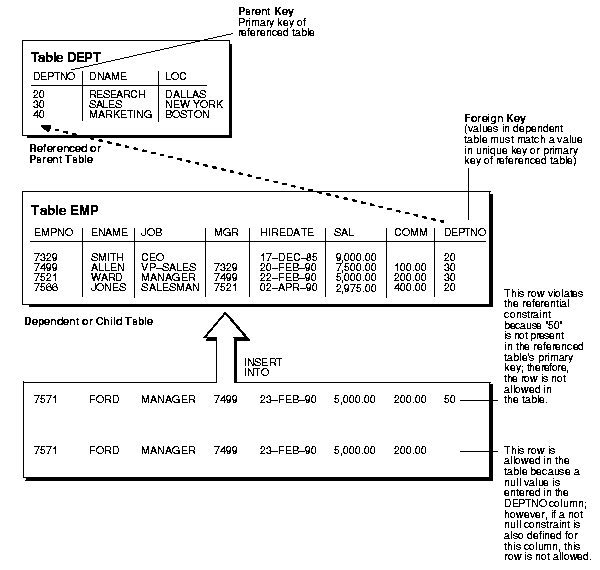
Several relationships between parent and child tables can be determined by the other types of integrity constraints defined on the foreign key in the child table.
When no other constraints are defined on the foreign key, any number of rows in the child table can reference the same parent key value. This model allows nulls in the foreign key.
This model establishes a "one-to-many" relationship between the parent and foreign keys that allows undetermined values (nulls) in the foreign key. An example of such a relationship is shown in Figure 4-3 on page 8 between EMP_TAB and DEPT_TAB; each department (parent key) has many employees (foreign key), and some employees might not be in a department (nulls in the foreign key).
When nulls are not allowed in a foreign key, each row in the child table must explicitly reference a value in the parent key because nulls are not allowed in the foreign key. However, any number of rows in the child table can reference the same parent key value.
This model establishes a "one-to-many" relationship between the parent and foreign keys. However, each row in the child table must have a reference to a parent key value; the absence of a value (a null) in the foreign key is not allowed. The same example in the previous section can be used to illustrate such a relationship. However, in this case, employees must have a reference to a specific department.
When a UNIQUE constraint is defined on the foreign key, one row in the child table can reference a parent key value. This model allows nulls in the foreign key.
This model establishes a "one-to-one" relationship between the parent and foreign keys that allows undetermined values (nulls) in the foreign key. For example, assume that the EMP_TAB table had a column named MEMBERNO, referring to an employee's membership number in the company's insurance plan. Also, a table named INSURANCE has a primary key named MEMBERNO, and other columns of the table keep respective information relating to an employee's insurance policy. The MEMBERNO in the EMP_TAB table should be both a foreign key and a unique key:
EMP_TAB and INSURANCE tables (the FOREIGN KEY constraint)
UNIQUE key constraint)
When both UNIQUE and NOT NULL constraints are defined on the foreign key, only one row in the child table can reference a parent key value. Because nulls are not allowed in the foreign key, each row in the child table must explicitly reference a value in the parent key.
This model establishes a "one-to-one" relationship between the parent and foreign keys that does not allow undetermined values (nulls) in the foreign key. If you expand the previous example by adding a NOT NULL constraint on the MEMBERNO column of the EMP_TAB table, in addition to guaranteeing that each employee has a unique membership number, then you also ensure that no undetermined values (nulls) are allowed in the MEMBERNO column of the EMP_TAB table.
Oracle allows a column to be referenced by multiple FOREIGN KEY constraints; effectively, there is no limit on the number of dependent keys. This situation might be present if a single column is part of two different composite foreign keys.
When Oracle checks a constraint, it signals an error if the constraint is not satisfied. You can defer checking the validity of constraints until the end of a transaction.
When you issue the SET CONSTRAINTS statement, the SET CONSTRAINTS mode lasts for the duration of the transaction, or until another SET CONSTRAINTS statement resets the mode.
See Also: For more details about the SET CONSTRAINTS statement, see the Oracle8i SQL Reference.
For general information about constraints, see Oracle8i Concepts.
You may wish to defer constraint checks on UNIQUE and FOREIGN keys if the data you are working with has any of the following characteristics:
When dealing with bulk data being manipulated by outside applications, you can defer checking constraints for validity until the end of a transaction.
After you have identified and selected the appropriate tables, make sure the tables' FOREIGN, UNIQUE and PRIMARY key constraints are created deferrable. You can do so by issuing a statement similar to the following:
CREATE TABLE dept ( deptno NUMBER PRIMARY KEY, dname VARCHAR2 (30) ); CREATE TABLE emp ( empno NUMBER, ename VARCHAR2 (30), deptno NUMBER REFERENCES (dept), CONSTRAINT epk PRIMARY KEY (empno) DEFERRABLE, CONSTRAINT efk FOREIGN KEY (deptno) REFERENCES (dept. deptno) DEFERRABLE); INSERT INTO dept VALUES (10, 'Accounting'); INSERT INTO dept VALUES (20, 'SALES'); INSERT INTO emp VALUES (1, 'Corleone', 10); INSERT INTO emp VALUES (2, 'Costanza', 20); COMMIT; SET CONSTRAINT efk DEFERRED; UPDATE dept SET deptno = deptno + 10 WHERE deptno = 20; SELECT * from emp ORDER BY deptno; EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO ----- -------------- ------- 1 Corleone 10 2 Costanza 20 UPDATE emp SET deptno = deptno + 10 WHERE deptno = 20; SELECT * FROM emp ORDER BY deptno; EMPNO ENAME DEPTNO ----- -------------- ------- 1 Corleone 10 2 Costanza 30 COMMIT;
Within the application being used to manipulate the data, you must set all constraints deferred before you actually begin processing any data. Use the following DML statement to set all deferrable constraints deferred:
SET CONSTRAINTS ALL DEFERRED;
You can check for constraint violations before committing by issuing the SET CONSTRAINTS ALL IMMEDIATE statement just before issuing the COMMIT. If there are any problems with a constraint, this statement will fail and the constraint causing the error will be identified. If you commit while constraints are violated, the transaction will be rolled back and you will receive an error message.
When you create a UNIQUE or PRIMARY key, Oracle checks to see if an existing index can be used to enforce uniqueness for the constraint. If there is no such index, Oracle creates one.
When Oracle is using a unique index to enforce a constraint, and constraints associated with the unique index are dropped or disabled, the index is dropped.
While enabled foreign keys reference a PRIMARY or UNIQUE key, you cannot disable or drop the PRIMARY or UNIQUE key constraint or the index.
You should almost always index foreign keys. The only exception is when the matching unique or primary key is never updated or deleted.
Oracle does not permit declarative referential integrity constraints to be defined across nodes of a distributed database (in other words, a declarative referential integrity constraint on one table cannot specify a foreign key that references a primary or unique key of a remote table).
However, parent/child table relationships across nodes can be maintained using triggers.
|
See Also:
For more information about triggers that enforce referential integrity, refer to Chapter 12, "Using Triggers". |
Use CHECK constraints when you need to enforce integrity rules based on logical expressions, such as comparisons. Never use CHECK constraints when any of the other types of integrity constraints can provide the necessary checking.
Examples of CHECK constraints include the following:
CHECK constraint on the SAL column of the EMP_TAB table so that no salary value is greater than 10000
CHECK constraint on the LOC column of the DEPT_TAB table so that only the locations "BOSTON", "NEW YORK", and "DALLAS" are allowed
CHECK constraint on the SAL and COMM columns to compare the SAL and COMM values of a row and prevent the COMM value from being greater than the SAL value
A CHECK integrity constraint requires that a condition be true or unknown for every row of the table. If a statement causes the condition to evaluate to false, then the statement is rolled back. The condition of a CHECK constraint has the following limitations:
SYSDATE, UID, USER, or USERENV SQL functions.
LEVEL, PRIOR, or ROWNUM;
When using CHECK constraints, consider the ANSI/ISO standard which states that a CHECK constraint is violated only if the condition evaluates to false; true and unknown values do not violate a check condition. Therefore, make sure that any CHECK constraint that you define actually enforces the rule you need enforced.
For example, consider the following CHECK constraint:
CHECK (Sal > 0 OR Comm >= 0)
At first glance, this rule may be interpreted as "do not allow a row in the EMP_TAB table unless the employee's salary is greater than zero or the employee's commission is greater than or equal to zero." However, note that if a row is inserted with a null salary and a negative commission, then the row does not violate the CHECK constraint, because the entire check condition is evaluated as unknown. In this particular case, you can account for such violations by placing NOT NULL integrity constraints on both the SAL and COMM columns.
|
Note:
If you are not sure when unknown values result in |
A single column can have multiple CHECK constraints that reference the column in its definition. There is no limit to the number of CHECK constraints that can be defined that reference a column.
The order in which the constraints are evaluated is not defined, so be careful not to rely on the order or to define multiple constraints that conflict with each other.
According to the ANSI/ISO standard, a NOT NULL integrity constraint is an example of a CHECK integrity constraint, where the condition is the following:
CHECK (Column_name IS NOT NULL)
Therefore, NOT NULL integrity constraints for a single column can, in practice, be written in two forms: using the NOT NULL constraint or a CHECK constraint. For ease of use, you should always choose to define NOT NULL integrity constraints, instead of CHECK constraints with the IS NOT NULL condition.
In the case where a composite key can allow only all nulls or all values, you must use a CHECK integrity constraint. For example, the following expression of a CHECK integrity constraint allows a key value in the composite key made up of columns C1 and C2 to contain either all nulls or all values:
CHECK ((C1 IS NULL AND C2 IS NULL) OR (C1 IS NOT NULL AND C2 IS NOT NULL))
Here are some examples showing how to create simple constraints during the prototype phase of your database design.
Notice how all constraints are given a name. Naming the constraints prevents the database from creating multiple copies of the same constraint, with different system-generated names, if the DDL is run multiple times.
|
See Also:
Oracle8i Administrator's Guide for information on creating and maintaining constraints for a large production database. |
The following examples of CREATE TABLE statements show the definition of several integrity constraints:
CREATE TABLE Dept_tab ( Deptno NUMBER(3) CONSTRAINT Dept_pkey PRIMARY KEY, Dname VARCHAR2(15), Loc VARCHAR2(15), CONSTRAINT Dname_ukey UNIQUE (Dname, Loc), CONSTRAINT Loc_check1 CHECK (loc IN ('NEW YORK', 'BOSTON', 'CHICAGO'))); CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( Empno NUMBER(5) CONSTRAINT Emp_pkey PRIMARY KEY, Ename VARCHAR2(15) NOT NULL, Job VARCHAR2(10), Mgr NUMBER(5) CONSTRAINT Mgr_fkey REFERENCES Emp_tab, Hiredate DATE, Sal NUMBER(7,2), Comm NUMBER(5,2), Deptno NUMBER(3) NOT NULL CONSTRAINT dept_fkey REFERENCES Dept_tab ON DELETE CASCADE);
You can also define integrity constraints using the constraint clause of the ALTER TABLE command. For example, the following examples of ALTER TABLE statements show the definition of several integrity constraints:
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX I_dept ON Dept_tab(deptno); ALTER TABLE Dept_tab ADD CONSTRAINT Dept_pkey PRIMARY KEY (deptno); ALTER TABLE Emp_tab ADD CONSTRAINT Dept_fkey FOREIGN KEY (Deptno) REFERENCES Dept_tab; ALTER TABLE Emp_tab MODIFY (Ename VARCHAR2(15) NOT NULL);
You cannot create a validated constraint on a table if the table already contains any rows that would violate the constraint.
The creator of a constraint must have the ability to create tables (the CREATE TABLE or CREATE ANY TABLE system privilege), or the ability to alter the table (the ALTER object privilege for the table or the ALTER ANY TABLE system privilege) with the constraint. Additionally, UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY integrity constraints require that the owner of the table have either a quota for the tablespace that contains the associated index or the UNLIMITED TABLESPACE system privilege. FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints also require some additional privileges.
Assign names to NOT NULL, UNIQUE KEY, PRIMARY KEY, FOREIGN KEY, and CHECK constraints using the CONSTRAINT option of the constraint clause. This name must be unique with respect to other constraints that you own. If you do not specify a constraint name, then one is assigned by Oracle.
Picking your own name makes error messages for constraint violations more understandable, and prevents the creation of multiple constraints if the SQL statements are run more than once.
See the previous examples of the CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements for examples of the CONSTRAINT option of the constraint clause. Note that the name of each constraint is included with other information about the constraint in the data dictionary.
Enabling and Disabling Integrity Constraints
This section explains the mechanisms and procedures for manually enabling and disabling integrity constraints.
In summary, an integrity constraint can be thought of as a statement about the data in a database. This statement is always true when the constraint is enabled; however, the statement may or may not be true when the constraint is disabled because data in violation of the integrity constraint can be in the database.
To enforce the rules defined by integrity constraints, the constraints should always be enabled; however, in certain situations, it is desirable to disable the integrity constraints of a table temporarily for performance reasons. For example:
In cases such as these, integrity constraints may be temporarily turned off to improve the performance of the operation.
If a row of a table does not adhere to an integrity constraint, then this row is said to be in violation of the constraint and is known as an exception to the constraint. If any exceptions exist, then the constraint cannot be enabled. The rows that violate the constraint must be either updated or deleted in order for the constraint to be enabled.
Exceptions for a specific integrity constraint can be identified while attempting to enable the constraint.
When you define an integrity constraint in a CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statement, you can enable the constraint by including the ENABLE clause in its definition or disable it by including the DISABLE clause in its definition. If neither the ENABLE nor the DISABLE clause is included in a constraint's definition, Oracle automatically enables the constraint.
The following CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements both define and enable integrity constraints:
CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( Empno NUMBER(5) PRIMARY KEY); ALTER TABLE Emp_tab ADD PRIMARY KEY (Empno);
An ALTER TABLE statement that defines and attempts to enable an integrity constraint may fail because rows of the table may violate the integrity constraint. In this case, the statement is rolled back and the constraint definition is not stored and not enabled.
The following CREATE TABLE and ALTER TABLE statements both define and disable integrity constraints:
CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( Empno NUMBER(5) PRIMARY KEY DISABLE); ALTER TABLE Emp_tab ADD PRIMARY KEY (Empno) DISABLE;
An ALTER TABLE statement that defines and disables an integrity constraints never fails. The definition of the constraint is always allowed because its rule is not enforced.
Use the ALTER TABLE command to
ENABLE clause
DISABLE clause
The following statements are examples of statements that enable disabled integrity constraints:
ALTER TABLE Dept_tab ENABLE CONSTRAINT Dname_ukey; ALTER TABLE Dept_tab ENABLE PRIMARY KEY ENABLE UNIQUE (Dname) ENABLE UNIQUE (Loc);
An ALTER TABLE statement that attempts to enable an integrity constraint fails when the rows of the table violate the integrity constraint. In this case, the statement is rolled back and the constraint is not enabled.
|
See Also:
1"Exception Reporting" for more information about rows that violate integrity constraints. |
The following statements are examples of statements that disable enabled integrity constraints:
ALTER TABLE Dept_tab DISABLE CONSTRAINT Dname_ukey; ALTER TABLE Dept_tab DISABLE PRIMARY KEY DISABLE UNIQUE (Dname) DISABLE UNIQUE (Loc);
|
Tip -- Using the Data Dictionary for Reference: The example statements in the previous sections require that you have some information about a constraint to enable or disable it. For example, the first statement of each section requires that you know the constraint's name, while the second statement of each section requires that you know the unique key's column list. If you do not have such information, then you can query one of the data dictionary views defined for constraints, USER_CONSTRAINTS or USER_CONS_COLUMNS; for more information about these views, see "Listing Integrity Constraint Definitions" and Oracle8i Reference. |
When enabling or disabling UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, and FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints, you should be aware of several important issues and prerequisites. UNIQUE key and PRIMARY KEY constraints are usually managed by the database administrator.
When you issue a CREATE TABLE... ENABLE... or ALTER TABLE... ENABLE... statement, and the statement is not successfully executed because integrity constraint exceptions exist, the statement is rolled back and you cannot enable the constraint until all exceptions to the constraint are either updated or deleted. To determine which rows violate the integrity constraint, include the EXCEPTIONS option in the ENABLE clause of a CREATE TABLE or ALTER TABLE statement.
In Oracle 8.0, only certain constraint states could be changed using the ENABLE or DISABLE clauses. With Oracle 8.1, there are expanded capabilities to alter the state of an existing constraint with the MODIFY CONSTRAINT clause.
|
See Also:
For information on the parameters you can modify, see the |
CREATE TABLE X1_tab (a1 NUMBER CONSTRAINT y CHECK (a1>3) DEFERRABLE DISABLE); ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY CONSTRAINTY_cnstrtENABLE; ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY CONSTRAINTY_cnstrtRELY; ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY CONSTRAINTY_cnstrtINITIALLY DEFERRED; ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY CONSTRAINTY_cnstrtENABLE NOVALIDATE;
CREATE TABLEX1_tab(A1 NUMBER CONSTRAINT Y_cnstrtNOT NULL DEFERRABLE INITIALLY DEFERRED NORELY DISABLE); ALTER TABLE X1_tab ADD CONSTRAINT One_cnstrt UNIQUE(A1) DEFERRABLE INITIALLY IMMEDIATE RELY USING INDEX PCTFREE = 30 ENABLE VALIDATE; ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY UNIQUE(A1) INITIALLY DEFERRED NORELY USING INDEX PCTFREE = 40 ENABLE NOVALIDATE; ALTER TABLE X1_tab MODIFY CONSTRAINT One_cnstrt INITIALLY IMMEDIATE RELY;
CREATE TABLE T1_tab (A1 INT, B1 INT); ALTER TABLE T1_tab add CONSTRAINT P1_cnstrt PRIMARY KEY(a1) DISABLE; ALTER TABLE T1_tab MODIFY PRIMARY KEY INITIALLY IMMEDIATE USING INDEX PCTFREE = 30 ENABLE NOVALIDATE; ALTER TABLE T1_tab MODIFY PRIMARY KEY USING INDEX PCTFREE = 35 ENABLE; ALTER TABLE T1_tab MODIFY PRIMARY KEY ENABLE NOVALIDATE;
Drop an integrity constraint if the rule that it enforces is no longer true or if the constraint is no longer needed. Drop an integrity constraint using the ALTER TABLE command and the DROP clause. For example, the following statements drop integrity constraints:
ALTER TABLE Dept_tab
DROP UNIQUE (Dname);
ALTER TABLE Dept_tab
DROP UNIQUE (Loc);
ALTER TABLE Emp_tab
DROP PRIMARY KEY,
DROP CONSTRAINT Dept_fkey;
DROP TABLE Emp_tab CASCADE CONSTRAINTS;
When dropping UNIQUE, PRIMARY KEY, and FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints, you should be aware of several important issues and prerequisites. UNIQUE and PRIMARY KEY constraints are usually managed by the database administrator.
General information about defining, enabling, disabling, and dropping all types of integrity constraints is given in the previous sections. The following section supplements this information, focusing specifically on issues regarding FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints.
The following topics are of interest when defining FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints.
When defining referential integrity constraints, the corresponding column names of the dependent and referenced tables do not need to match. However, they must be of the same datatype.
Because foreign keys reference primary and unique keys of the parent table, and PRIMARY KEY and UNIQUE key constraints are enforced using indexes, composite foreign keys are limited to 32 columns.
If the column list is not included in the REFERENCES option when defining a FOREIGN KEY constraint (single column or composite), then Oracle assumes that you intend to reference the primary key of the specified table. Alternatively, you can explicitly specify the column(s) to reference in the parent table within parentheses. Oracle automatically checks to verify that this column list references a primary or unique key of the parent table. If it does not, then an informative error is returned.
To create a FOREIGN KEY constraint, the creator of the constraint must have privileged access to both the parent and the child table.
REFERENCES object privileges on the columns that constitute the parent key of the parent table.
CREATE TABLE or CREATE ANY TABLE system privilege) or the ability to alter the child table (that is, the ALTER object privilege for the child table or the ALTER ANY TABLE system privilege).
In both cases, necessary privileges cannot be obtained via a role; they must be explicitly granted to the creator of the constraint.
These restrictions allow:
Oracle allows different types of referential integrity actions to be enforced, as specified with the definition of a FOREIGN KEY constraint:
FOREIGN KEY constraints enforce the no action restriction; no option needs to be specified when defining the constraint to enforce the no action restriction. For example:
CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( FOREIGN KEY (Deptno) REFERENCES Dept_tab);
ON DELETE CASCADE option in the definition of the FOREIGN KEY constraint. For example:
CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( FOREIGN KEY (Deptno) REFERENCES Dept_tab ON DELETE CASCADE);
ON DELETE SET NULL option in the definition of the FOREIGN KEY constraint. For example:
CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( FOREIGN KEY (Deptno) REFERENCES Dept_tab ON DELETE SET NULL);
FOREIGN KEY integrity constraints cannot be enabled if the referenced primary or unique key's constraint is not present or not enabled.
The data dictionary contains the following views that relate to integrity constraints:
ALL_CONSTRAINTS
ALL_CONS_COLUMNS
CONSTRAINT_COLUMNS
CONSTRAINT_DEFS
USER_CONSTRAINTS
USER_CONS_COLUMNS
USER_CROSS_REFS
DBA_CONSTRAINTS
DBA_CONS_COLUMNS
DBA_CROSS_REFS
Consider the following CREATE TABLE statements that define a number of integrity constraints:
CREATE TABLE Dept_tab ( Deptno NUMBER(3) PRIMARY KEY, Dname VARCHAR2(15), Loc VARCHAR2(15), CONSTRAINT Dname_ukey UNIQUE (Dname, Loc), CONSTRAINT LOC_CHECK1 CHECK (Loc IN ('NEW YORK', 'BOSTON', 'CHICAGO'))); CREATE TABLE Emp_tab ( Empno NUMBER(5) PRIMARY KEY, Ename VARCHAR2(15) NOT NULL, Job VARCHAR2(10), Mgr NUMBER(5) CONSTRAINT Mgr_fkey REFERENCES Emp_tab ON DELETE CASCADE, Hiredate DATE, Sal NUMBER(7,2), Comm NUMBER(5,2), Deptno NUMBER(3) NOT NULL CONSTRAINT Dept_fkey REFERENCES Dept_tab);
The following query lists all constraints defined on all tables accessible to the user:
SELECT Constraint_name, Constraint_type, Table_name, R_constraint_name FROM User_constraints;
Considering the example statements at the beginning of this section, a list similar to the one below is returned:
CONSTRAINT_NAME C TABLE_NAME R_CONSTRAINT_NAME --------------- - ----------- ------------------ SYS_C00275 P DEPT_TAB DNAME_UKEY U DEPT_TAB LOC_CHECK1 C DEPT_TAB SYS_C00278 C EMP_TAB SYS_C00279 C EMP_TAB SYS_C00280 P EMP_TAB MGR_FKEY R EMP_TAB SYS_C00280 DEPT_FKEY R EMP_TAB SYS_C00275
Notice the following:
DNAME_UKEY), while others are system specified (such as SYS_C00275).
CONSTRAINT_TYPE column. The table below summarizes the characters used for each constraint type.
| Constraint Type | Character |
|
|
P |
|
|
U |
|
|
R |
|
|
C |
|
Note:
An additional constraint type is indicated by the character "V" in the |
In the previous example, several constraints are listed with a constraint type of "C". To distinguish which constraints are NOT NULL constraints and which are CHECK constraints in the EMP_TAB and DEPT_TAB tables, issue the following query:
SELECT Constraint_name, Search_condition FROM User_constraints WHERE (Table_name = 'DEPT_TAB' OR Table_name = 'EMP_TAB') AND Constraint_type = 'C';
Considering the example CREATE TABLE statements at the beginning of this section, a list similar to the one below is returned:
CONSTRAINT_NAME SEARCH_CONDITION --------------- ---------------------------------------- LOC_CHECK1 loc IN ('NEW YORK', 'BOSTON', 'CHICAGO') SYS_C00278 ENAME IS NOT NULL SYS_C00279 DEPTNO IS NOT NULL
Notice the following:
NOT NULL constraints are clearly identified in the SEARCH_CONDITION column.
CHECK constraints are explicitly listed in the SEARCH_CONDITION column.
The following query lists all columns that constitute the constraints defined on all tables accessible to you, the user:
SELECT Constraint_name, Table_name, Column_name FROM User_cons_columns;
Considering the example statements at the beginning of this section, a list similar to the one below is returned:
CONSTRAINT_NAME TABLE_NAME COLUMN_NAME --------------- ----------- --------------- DEPT_FKEY EMP_TAB DEPTNO DNAME_UKEY DEPT_TAB DNAME DNAME_UKEY DEPT_TAB LOC LOC_CHECK1 DEPT_TAB LOC MGR_FKEY EMP_TAB MGR SYS_C00275 DEPT_TAB DEPTNO SYS_C00278 EMP_TAB ENAME SYS_C00279 EMP_TAB DEPTNO SYS_C00280 EMP_TAB EMPNO
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|