Release 2 (8.1.6)
Part Number A76990-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Recovery Manager User's Guide and Reference Release 2 (8.1.6) Part Number A76990-01 |
|
Recovery Manager Command Syntax, 43 of 50
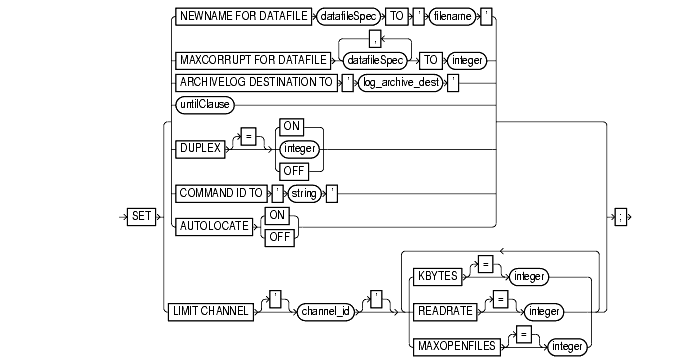
To set attributes for a run command that persist until the end of the job. The specified attributes affect all statements within run that follow the set command. Use set to:
|
sets the default name for all subsequent restore or switch commands that affect the specified datafile (see "datafileSpec"). If you do not issue this command before the datafile restore operation, then RMAN restores the file to its default location. |
||
|
sets a limit on the number of previously undetected physical block corruptions that Oracle will allow in a specified datafile or list of datafiles (see "datafileSpec"). If a backup or copy command detects more than the specified number of corruptions, the command aborts. The default limit is zero, meaning that RMAN tolerates no corrupt blocks. Note: If you specify check logical, then the maxcorrupt limit applies to logical corruptions as well. |
||
|
autolocate |
forces RMAN to automatically discover which nodes of an OPS cluster contain the backups that you want to restore. Set to on or off (default). This option forces RMAN to hunt for backups on all allocated channels and to restore backups only from those channels that locate the backups on tape or on a filesystem. For example, assume that nodes A, B, and C are in an OPS configuration. If node A backs up a datafile to a tape drive or local filesystem, you must tell RMAN not to attempt to restore from nodes A or B. The set autolocate command performs this function. Issue the set autolocate on command only if: |
|
|
archivelog destination to 'log_archive_dest' |
overrides the LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST or LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 initialization parameter in the target database when forming names for restored archive logs during subsequent restore and recover commands. RMAN restores the logs to the destination specified in 'log_archive_dest'. Use this parameter to restore archived redo logs that are not already on disk. Use this command to stage many archived logs to different locations while a database restore is occurring. RMAN knows where to find the newly restored archive logs; it does not require them to be in the destination specified by LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_1 or LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST. For example, if you specify a different destination from the one in the parameter file and restore archived redo log backups, subsequent restore and recovery operations will detect this new location. RMAN always looks for archived redo logs on disk first before restoring them from backup sets. |
|
|
untilClause |
specifies an end time, SCN, or log sequence number for a subsequent restore or recover command. See "untilClause". |
|
|
duplex |
specifies the number of copies of each backup piece that the channels should create: 1, 2, 3, or 4. The set duplex command, which affects only the backup command, affects all channels allocated after issuing the command and is in effect until explicitly disabled (off) or changed during the session. By default duplex is off, that is, RMAN produces a single backup set. If you specify on, RMAN produces two identical backup sets. |
|
|
command id to 'string' |
enters the specified string into the V$SESSION.CLIENT_INFO column of all channels. Use this information to determine which Oracle server sessions correspond to which RMAN channels. The V$SESSION.CLIENT_INFO column contains information for each RMAN server session. The data appears in one of the following formats: The first form appears in the RMAN target database connection. The second form appears in all allocated channels. When the current job is complete, the V$SESSION.CLIENT_INFO column will be cleared. See Also: Oracle8i Reference for more information on V$SESSION.CLIENT_INFO. |
|
|
limit channel channel_id |
sets parameters that specify limits applying to any backup or copy command that executes using the allocated channel. |
|
|
|
kbytes integer |
specifies the maximum size in kilobytes of the backup pieces created on this channel. |
|
|
readrate integer |
specifies the maximum number of buffers (each of size DB_BLOCKSIZE * DB_FILE_DIRECT_IO_COUNT) per second read for backup or copy operations from each of the input datafiles. By default, this parameter is not set. Use this parameter to "throttle back" RMAN, that is, set an upper limit for block reads so that RMAN does not consume excessive disk bandwidth and thereby degrade online performance. See Also: Oracle8i Designing and Tuning for Performance for more information. |
|
|
maxopenfiles integer |
controls the maximum number of input files that a backup command can have open at any given time. Use this parameter to prevent "Too many open files" operating system error messages when backing up a large number of files into a single backup set. If you do not specify maxopenfiles, then a maximum of 32 input files can be open concurrently. |
This example sets the command ID, backs up the DATA_1 tablespace, hosts out to the operating system, then archives the online redo logs:
run {
set command id to 'rman';
allocate channel t1 type 'SBT_TAPE'
allocate channel t2 type 'SBT_TAPE';
backup
incremental level 0
filesperset 5
tablespace data_1;
host;
sql 'ALTER SYSTEM ARCHIVE LOG ALL';
}
This example makes two identical backup sets of datafile 1:
run { set duplex = ON; allocate channel dev1 type disk; backup filesperset 1 datafile 1; }
This example allocates three channels and sets the maximum size for backup pieces created on each channel. It also makes three identical backups of the database:
startup mount; run { set duplex=3; allocate channel ch1 type 'sbt_tape'; allocate channel ch2 type 'sbt_tape'; allocate channel ch3 type 'sbt_tape'; set limit channel ch1 kbytes 2097150; set limit channel ch2 kbytes 2097150; set limit channel ch3 kbytes 2907150; backup filesperset 5 database; alter database open; }
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|