Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A85397-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A85397-01 |
|
SQL Statements:
CREATE CLUSTER to CREATE SEQUENCE, 15 of 25
Use the CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG statement to create a materialized view log, which is a table associated with the master table of a materialized view. The terms snapshot and materialized view are synonymous. Both refer to a table that contains the results of a query of one or more tables, each of which may be located on the same or on a remote database.
When DML changes are made to the master table's data, Oracle stores rows describing those changes in the materialized view log and then uses the materialized view log to refresh materialized views based on the master table. This process is called a fast refresh. Without a materialized view log, Oracle must reexecute the materialized view query to refresh the materialized view. This process is called a complete refresh. Usually, a fast refresh takes less time than a complete refresh.
A materialized view log is located in the master database in the same schema as the master table. You need only a single materialized view log for a master table. Oracle can use this materialized view log to perform fast refreshes for all fast-refreshable materialized views based on the master table.
To fast refresh a materialized join view (a materialized view containing a join), you must create a materialized view log for each of its master tables.
|
See Also:
|
The privileges required to create a materialized view log directly relate to the privileges necessary to create the underlying objects associated with a materialized view log.
CREATE TABLE privilege.
CREATE ANY TABLE and COMMENT ANY TABLE privileges, as well as either the SELECT privilege for the master table or SELECT ANY TABLE.
In either case, the owner of the materialized view log must have sufficient quota in the tablespace intended to hold the materialized view log or must have the UNLIMITED TABLESPACE system privilege.
|
See Also:
Oracle8i Data Warehousing Guide for more information about the prerequisites for creating a materialized view log |
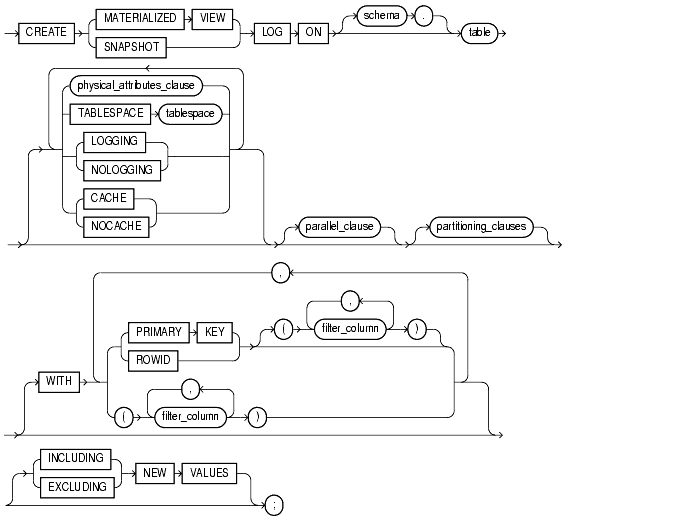

storage_clause: See storage_clause.

partitioning_clauses: See table_properties CREATE TABLE.
schema
Specify the schema containing the materialized view log's master table. If you omit schema, Oracle assumes the master table is contained in your own schema. Oracle creates the materialized view log in the schema of its master table. You cannot create a materialized view log for a table in the schema of the user SYS.
table
Specify the name of the master table for which the materialized view log is to be created. You cannot create a materialized view log for a view.
physical_attributes_clause
Use the physical_attributes_clause to establish values for physical and storage characteristics for the materialized view log.
TABLESPACE
Specify the tablespace in which the materialized view log is to be created. If you omit this clause, Oracle creates the materialized view log in the default tablespace of the owner of the materialized view log's schema.
LOGGING | NOLOGGING
Specify either LOGGING or NOLOGGING to establish the logging characteristics for the materialized view log.
CACHE | NOCACHE
For data that will be accessed frequently, CACHE specifies that the blocks retrieved for this log are placed at the most recently used end of the LRU list in the buffer cache when a full table scan is performed. This attribute is useful for small lookup tables. NOCACHE specifies that the blocks are placed at the least recently used end of the LRU list.
parallel_clause
The parallel_clause lets you indicate whether parallel operations will be supported for the materialized view log.
partitioning_clauses
Use the partitioning_clauses to indicate that the materialized view log is partitioned on specified ranges of values or on a hash function. Partitioning of materialized view logs is the same as partitioning of tables, as described in CREATE TABLE.
WITH
Use the WITH clause to indicate whether the materialized view log should record the primary key, the rowid, or both the primary key and rowid when rows in the master are updated.
This clause also specifies whether the materialized view log records filter columns, which are non-primary-key columns referenced by subquery materialized views.
If you omit this clause, primary key values are stored by default. Primary key values are implicitly stored when you specify a filter column list by itself. However, primary key values are not implicitly stored if you specify only ROWID or ROWID (filter_column) at create time.
Restrictions:
PRIMARY KEY, one ROWID, and one filter column list specification per materialized view log.
PRIMARY KEY is implicitly included in filter_column, you cannot specify either of the following combinations:
ADD PRIMARY KEY,(filter_column) ADD (filter_column), PRIMARY KEY
NEW VALUES
The NEW VALUES clause lets you indicate whether Oracle saves both old and new values in the materialized view log.
The following statement creates a materialized view log on an employee table that records only primary key values:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON emp WITH PRIMARY KEY;
Oracle can use this materialized view log to perform a fast refresh on any simple primary key materialized view subsequently created on the emp table.
The following statement also creates a materialized view log that record only the primary keys of updated rows:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON emp PCTFREE 5 TABLESPACE users STORAGE (INITIAL 10K NEXT 10K);
ROWID Example
The following statement creates a materialized view log that records both the primary keys and the rowids of updated rows:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON sales WITH ROWID, PRIMARY KEY;
The following statement creates a materialized view log that records primary keys and updates to the filter column zip:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON address WITH (zip);
NEW VALUES Example
The following example creates a master table, then creates a materialized view log that specifies INCLUDING NEW VALUES:
CREATE TABLE agg (u NUMBER, a NUMBER, b NUMBER, c NUMBER, d NUMBER); CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG ON agg WITH ROWID (u,a,b,c,d) INCLUDING NEW VALUES;
You could create the following materialized aggregate view to use the agg log:
CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW sn0 REFRESH FAST ON COMMIT AS SELECT SUM(b+c), COUNT(*), a, d, COUNT(b+c) FROM agg GROUP BY a,d;
This materialized view is eligible for fast refresh because the log it uses includes both old and new values.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|