Release 2 (8.1.6) for Windows
Part Number A73017-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Client Administrator's Guide Release 2 (8.1.6) for Windows Part Number A73017-01 |
|
This chapter describes how to enable Oracle8i directory features with Microsoft's Active Directory.
Specific topics discussed are:
This section provides an overview of the following topics:
The Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is a networking and directory access protocol for accessing information in a directory server. The directory server centrally stores and manages information about all network resources and makes that information accessible to users and applications. Resources can include user names, databases, computers, fax servers, applications, e-mail addresses, and printers. A directory server is analogous to a telephone directory, which stores information such as phone numbers and addresses of telephone subscribers.
Active Directory is the LDAP-compliant directory server included with Windows 2000. Active Directory centrally stores all Windows 2000 information, including users, groups, and policies. Active Directory also stores information about network resources such as databases, and makes this information available to application users and network administrators. Active Directory enables users to access network resources with a single login. The scope of Active Directory can range from storing all the resources of a small computer network to storing all the resources of several wide areas networks (WANs).
With Oracle8i release 8.1.6, two new features are provided for storing Oracle information in a directory server. These new features are briefly described in the following sections:
References are provided to additional documentation. Both features have been enabled to work with Microsoft's Active Directory.
This feature enables you to create and store database service and net service name entries for use with Net8 as directory objects in Active Directory. These objects contain connectivity information that can be used by various Oracle client applications when connecting to an Oracle8i database.
During Oracle8i release 8.1.6 database creation, a database service entry is created with Oracle Database Configuration Assistant. Clients configured to access the directory server can use this entry in their connect strings to connect to the database without any additional configuration.
If you prefer not to expose the database service entry to clients, you can use Net8 Assistant to create net service name entries in the directory server, which eliminates the need to create and maintain separate TNSNAMES.ORA files on each client computer. When clients attempt an Oracle8i database connection, the net service name is instead retrieved from a directory server. The Directory Server Migration Wizard, available with Net8 Assistant, enables you to export net service names stored in an existing TNSNAMES.ORA file to the directory server.
|
Note: Database service and net service name entries stored in an Oracle Names server can migrated to a directory server using the NAMESCTL utility. See the Net8 Administrator's Guide for more information. |
This chapter frequently references Net8 directory naming terms and concepts. Read the following documentation for descriptions of terms and concepts that an administrator and client user must understand before using an Oracle8i database with Active Directory.
| See Section... | Which Describes... |
|---|---|
|
"Net8 and an LDAP-Compliant Directory Server" in Chapter 2 of the Net8 Administrator's Guide |
|
|
"Configuring the Directory Naming Method" in Chapter 6 of the Net8 Administrator's Guide |
|
This feature enables you to create and store Oracle8i information as directory objects in Active Directory. This enables users to make natively-authenticated, Single Sign-On (SSO) connections to a database. An administrator can create and store enterprise users and roles for the Oracle8i in Active Directory, which helps centralize the administration of users and roles across multiple databases.
This chapter frequently references enterprise user security terms and concepts. Read the following documentation for descriptions of terms and concepts that an administrator and client user must understand before using an Oracle8i database with Active Directory.
| See... | Which Describes... |
|---|---|
|
Chapter 17, "Managing Enterprise User Security" of Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide |
|
|
Chapter 20, "Using Oracle Enterprise Security Manager" of Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide |
In addition to Net8 directory naming and enterprise user security integration with a directory server, the following features have been specifically integrated into Active Directory:
Net8 Configuration Assistant enables you to configure client computer and Oracle8i database server access to a directory server. When Net8 Configuration Assistant starts at the end of Oracle8i database installation or is manually started after installation, it prompts you to specify a directory server type to use. When you select Active Directory as your directory server type, Net8 Configuration Assistant automatically:
If the Active Directory server through which client connections are accessing an Oracle8i database is shut down, another Active Directory server is automatically discovered and begins providing connection information; this prevents any downtime for client connections.
You must be running your Oracle client and database software in a Windows 2000 domain to take advantage of the automatic directory server discovery features of Net8 Configuration Assistant. This is regardless of the Oracle client and database releases you are using.
If you are not running in a Windows 2000 domain, Net8 Configuration Assistant does not automatically discover your directory server, and instead prompts you for additional information, such as the naming context and Active Directory location.
Oracle8i database service, Net8 net service name, and enterprise role entries in Active Directory display in the following Microsoft Windows 2000 tools:
The property menus of Oracle8i database service and net service name objects in Windows Explorer and Active Directory Users and Computers have been enhanced. These enhancements enable you to test for object connectivity to the Oracle8i database and perform database administration. When you right click these Oracle directory objects, a menu presents you with two options for testing connectivity:
Oracle directory object type descriptions in Active Directory have been enhanced to make them easier to understand. For example, here is the description for OracleDefaultDomain's type in the Type column of the right window pane:
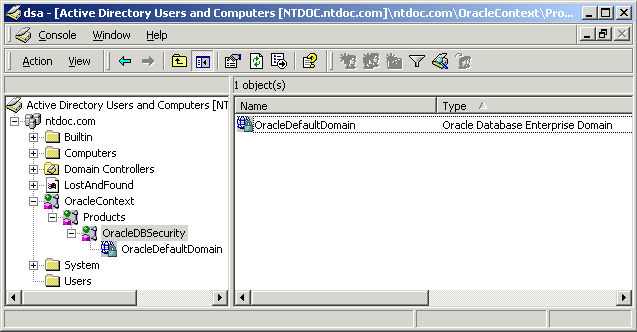
SSO enables client users to access all authorized network resources (such as Active Directory) with a single authentication that is performed when they initially specify their user login credentials to access the network. SSO is included in Windows 2000 through the Kerberos and Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) authentication protocols.
The Oracle8i database and configuration tools can use the Windows user's login credentials to automatically connect to Active Directory without having to re-enter their login credentials. This enables:
For Windows 2000, the default authentication protocol used is Kerberos.
When the Oracle8i database and Net8 are installed and configured to access Active Directory, Oracle directory objects appear in Active Directory Users and Computers:
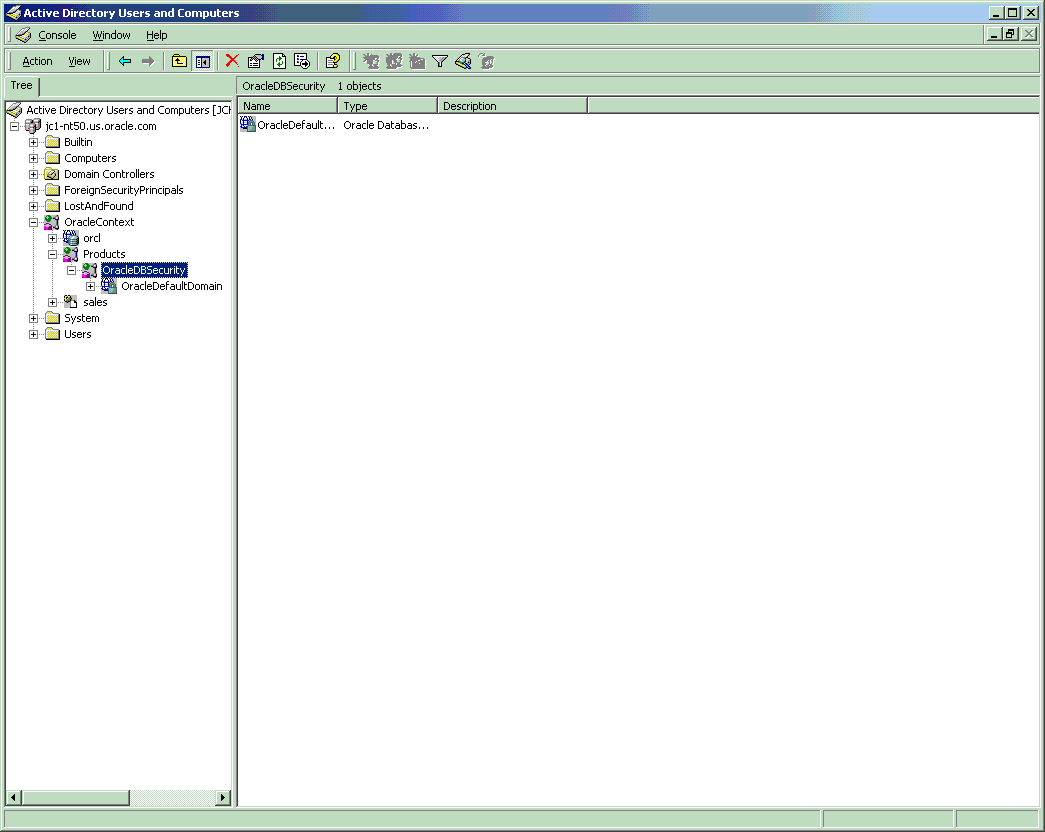
This table describes these Oracle directory objects:
| Object | Description |
|---|---|
|
domain |
The domain (also known as the administrative context) in which you created your Oracle Context. The administrative context contains various Oracle entries to support directory naming and enterprise user security. Net8 Configuration Assistant automatically discovers this information during Oracle8i database integration with Active Directory. |
|
OracleContext |
The top-level Oracle entry in the Active Directory tree that can contain Oracle8i database service and Net8 net service name object information. All Oracle software information is placed in this container. |
|
orcl |
The Oracle8i database service name (for this example, orcl is the name). |
|
Products |
A container for Oracle security and domain information. |
|
OracleDBSecurity |
A container for security domains. |
|
OracleDefaultDomain |
The default enterprise domain created. You can create additional enterprise domains with Oracle Enterprise Security Manager. |
|
sales |
The net service name object (for this example, sales is the name). |
|
Users |
The folder for the three Oracle security groups. See section "Managing Access Control Lists for Oracle Directory Objects" for more information. Enterprise users and roles created with Oracle Enterprise Security Manager also appear in this folder. |
The requirements that you must complete depend upon the Oracle features you want to use:
| Required For... | ||
|---|---|---|
| Requirement | Net8 Directory Naming? | Enterprise User Security? |
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
Yes |
|
|
Yes |
No |
|
|
No |
Yes |
|
Complete the following Oracle schema creation requirements to use the Net8 directory naming and enterprise user security features with Active Directory. A schema is a set of rules for Net8 and Oracle8i database entries and their attributes stored in Active Directory.
Net8 Administrator's Guide for configuration procedures and Oracle8i Client Installation Guide for Windows for a configuration overview.
See Also:
You must complete the following Oracle Context creation requirements to use the Net8 directory naming and enterprise user security features with Active Directory. The Oracle Context is the top-level Oracle entry in the Active Directory tree that contains Oracle8i database service and Net8 net service name object information.
Oracle8i Client Installation Guide for Windows for installation procedures and the Net8 Administrator's Guide for configuration procedures
See Also:
Ensure that you first satisfy the requirements described in:
This table describes the Microsoft and Oracle software releases that must be installed to use Net8 directory naming with Active Directory:
| For... | The Required Microsoft Software Is... | The Required Oracle Software Is... |
|---|---|---|
|
Client Computers |
Oracle8i Client release 8.1.6, which includes Net8 Client and these configuration tools: Note: See the Oracle8i Client Installation Guide for Windows for installation instructions and "Required Configuration Tools" for descriptions of the tasks that these configuration tools perform. |
|
|
Database Server |
Oracle8i database release 8.1.6 is required for registering the database service as an object in Active Directory. |
Ensure that you first satisfy the requirements described in:
This table describes the Microsoft and Oracle software releases required to use enterprise user security with Active Directory:
This section provides an overview of installation and configuration information. Specific topics covered include:
See Chapters 4 and 5 of the Oracle8i Client Installation Guide for Windows for Oracle8i installation instructions.
Several tools are required for configuring the Oracle clients and Oracle8i database for access to Active Directory. This table identifies:
These tools are listed in the order in which to use them. After you configure your environment, you can take advantage of the Net8 directory naming and enterprise user security features.
| To... | Run this Tool... | When Does This Tool Run? | For More Information... |
|---|---|---|---|
|
Create an Oracle schema and Oracle Context in Active Directory (if one is not already installed) Set up Access Control Lists for security in Active Directory |
Net8 Configuration Assistant, which guides you through Oracle8i database server configuration with Active Directory. Run this tool either on the Oracle8i database server or from a client computer that connects to the server. |
There are two methods: |
|
|
Register the Oracle8i database as an object in Active Directory Note: This task is not required if you are not using the enterprise user security feature.
|
Oracle Database Configuration Assistant |
There are two methods:
|
|
|
Configure an Oracle8i client computer to access Active Directory |
Net8 Configuration Assistant, which guides you through client computer configuration with Active Directory by prompting you to: |
There are two methods for running Net8 Configuration Assistant: |
|
|
Create and modify net service name objects or modify Net8 attributes of the database |
Net8 Assistant |
You must manually start Net8 Assistant. |
|
|
Create enterprise users, roles, and domains in Active Directory (enterprise user security) |
Oracle Enterprise Security Manager |
Manually started as an integrated application of Oracle Enterprise Manager Console |
You must set the OSAUTH_X509_NAME registry parameter to TRUE to use enterprise user security.
This section describes how to connect to an Oracle8i database through Active Directory. Specific topics discussed include:
Client computers connect to an Oracle8i database by specifying the database entry that appears in the Oracle Context. For example, if the database service entry under the Oracle Context in Active Directory was sales, a user connects through SQL*Plus to the Oracle8i database as follows:
The connect strings in this table follow DNS-style conventions. While Active Directory also supports connections using X.500 naming conventions, DNS-style conventions are the recommended method because of ease of use. DNS-style conventions enable client users to access an Oracle8i database through a directory server by entering minimal connection information; this is the case even when the client computer and Oracle8i database are in separate domains. X.500 names are longer; this is especially the case when the client and Oracle8i database are located in different domains (also known as administrative contexts).
To learn more about X.500 naming conventions, see Chapter 2, "Net8 Concepts", of the Net8 Administrator's Guide for information.
Oracle directory objects in Active Directory are integrated with Microsoft tools such as:
You can perform the following tasks from within these Microsoft tools:
To access connectivity tools:
| With... | Choose... |
|---|---|
|
Active Directory Users and Computers |
|
|
Windows Explorer |
A menu appears with several options:
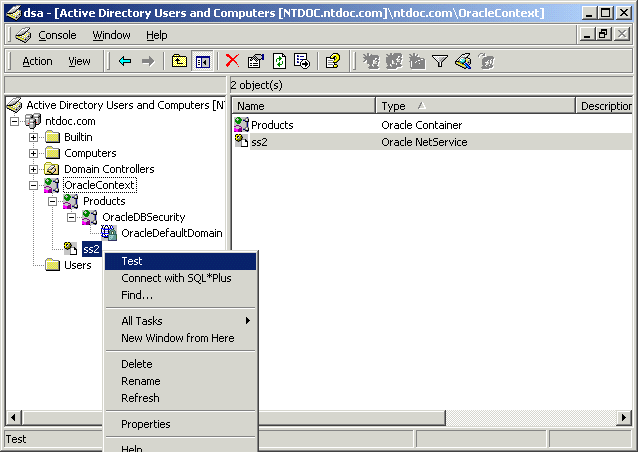
| If You Want To... | Then... |
|---|---|
|
Test connectivity |
|
|
Connect with SQL*Plus |
|
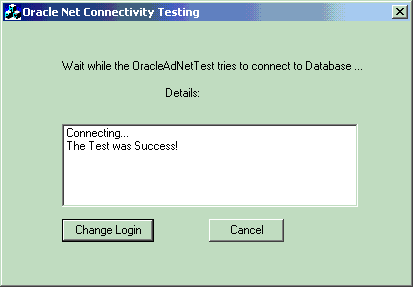
A status message appears describing the status of your connection attempt:
The Oracle SQL*Plus Login dialog box appears:
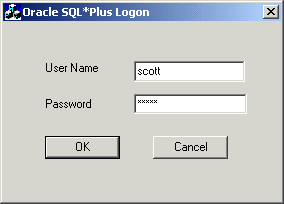
A status message appears describing the status of your connection attempt.
Access Control Lists provide Active Directory security by specifying:
Three security groups are automatically created when the Oracle Context is created in Active Directory. The user configuring access (and thus creating the Oracle Context) is automatically added to each:
Active Directory Users and Computers enables you to add or remove users or change permission settings in the three security groups.
There are several tools available for adding or removing users:
This section describes how to use Active Directory Users and Computers. See the Oracle Advanced Security Administrator's Guide for instructions on using Oracle Enterprise Security Manager.
To add or remove users or change permission settings:
This enables you to view and edit information that is normally hidden.
The three security groups appear in the right window pane:
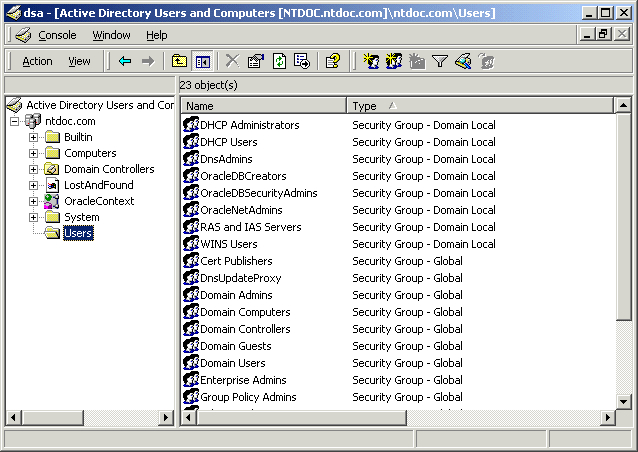
A menu appears with several options.
| If You Want To... | Then... |
|---|---|
|
Add or remove users |
|
|
Change permissions |
|
To add or remove users:
The Properties dialog box for the group you selected appears (in this example, OracleDBSecurityAdmins):
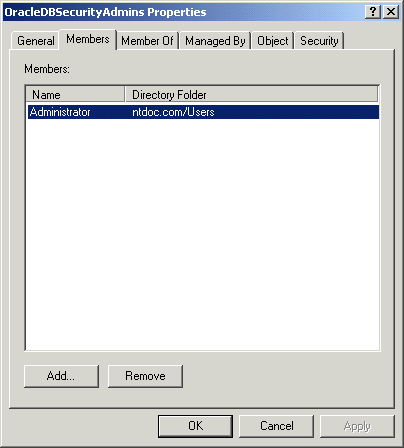
| To... | Then... |
|---|---|
|
Add Users |
|
|
Remove Users |
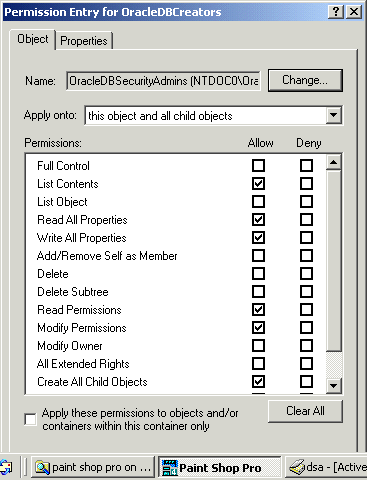
To change user permissions:
The Properties dialog box for the group you selected appears.
The Permission Entry dialog box for the security group you selected appears:
A default security domain, OracleDefaultDomain, is created in your Oracle Context. If you do not want to use this domain or want to create another domain, use Oracle Enterprise Security Manager to create additional security domains (called enterprise domains). These domains are added under the OracleDBSecurity folder.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|