Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A83728-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Java Developer's Guide Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A83728-01 |
|
JServer furnishes a debugging capability useful for developers who use the JDK's jdb debugger. Oracle's JDeveloper provides a user-friendly integration with this JServer debugging feature. See the JDeveloper documentation for more information on how to debug your Java application through JDeveloper. Other independent IDE vendors will be able to integrate their own debuggers with JServer.
The Sun Microsystems jdb debugger attaches itself to an executing process, and helps you debug the executing process. The application that you are debugging must have been compiled with the debug option (-g).
In JServer, your Java program executes remotely on a server. The server can reside on the same physical machine, but it typically resides on a separate machine. Oracle8i provides a method for jdb to debug a Java application loaded into JServer.
This method involves an debug agent that is executing on the Oracle8i server and communicating with the executing Java application, a debug proxy that exists on the client and communicates with the Oracle8i server, and a way for jdb to attach itself to the debug proxy. Figure 3-1 shows the relationship between the debug agent, the debug proxy, and the jdb debugger.
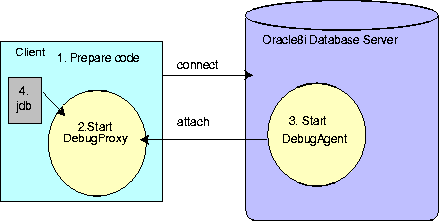
As shown in Figure 3-1, the steps for remotely debugging your Java application are as follows:
DebugProxy. The DebugProxy waits for a DebugAgent to attach to it from the server.
DebugAgent giving it the debug proxy address. This starts the communication between the debug agent and the debug proxy.
jdb debugger to the debug proxy. Once attached, you can use the regular jdb commands.
The code must be compiled with the -g option and the source must be made available for the debug agent to locate.
You can cause your application to be compiled with the debug option (-g) in one of the two following ways:
set_compiler_option procedure, as follows:
SQL> call dbms_java.set_compiler_option('myPackage.myCode','debug','true');
Then, you must load the source code using loadjava, as follows:
% loadjava -u SCOTT/TIGER -v -f -r myCode.java
The server will compile this class with the debug option. Also, the server now has access to both the source and the compiled binary, which the debug agent needs for showing the breakpoints.
g option, load the compiled class into the server, and copy the Java source file to the file system where Oracle8i JServer exists, as follows:
% javac -g MyCode.java % loadjava -u SCOTT/TIGER -v -f -r myCode.class % ftp dbhost > cd /private/sourcecode > put myCode.java
When jdb starts, set the location of the source code with jdb's 'use' command. This enables the debug agent to find the source code.
> use /private/sourcecode
The DebugProxy class enables your remote Java application appear to be local. The debug proxy forwards all jdb requests to the debug agent on the server and returns the results to the attached jdb debugger.
Once started, the debug proxy waits for the debug agent to attach itself. Assuming the aurora_client.jar file is part of your CLASSPATH, you start the debug proxy as follows:
debugproxy
You can also specify a particular port to wait on.
debugproxy -port 2286
The proxy prints out its name, its address, and the port it is waiting on.
Proxy Name: yourmachinename Proxy Address: aaa.bbb.ccc.ddd Proxy Port: 2286
However, the easiest method to start the DebugProxy is to append a command to start up the jdb debugger at the end of the debugproxy command. The debugproxy command takes in any option given, beyond the optional port, as a command to execute after it has started. If you choose this method, you do not need to execute step 4.
For UNIX, provide the following within an executable shell script called startjdb:
#!/bin/sh xterm -e jdb -password &1 &
Then, you can automatically start up the jdb debugger within the debugproxy command, as follows:
debugproxy -port 1638 startjdb
For all Windows NT environments, provide the following within a batch file called startjdb.bat:
start jdb -password %1
Then, you can automatically start up the jdb debugger within the debugproxy command, as follows:
debugproxy -port 1638 startjdb.bat
After you connect to the server (starting a session) and start a debug proxy, you can start a debug agent on the server that will connect to the proxy. When the DebugAgent starts, the DebugProxy displays a password to use when attaching the debugger in step 4.
|
Note: You must have the debug permission, JAVADEBUGPRIV, granted to your user to run a debug agent. See "Debugging Permissions" in the Oracle8i Java Developer's Guide for more information. |
Once a proxy is running, you can start a debug agent to connect to the proxy from SQL*Plus. You must specify the IP address or URL for a machine running a debug proxy, the port the proxy is waiting on, and a timeout in seconds. You start and stop the debug agent using methods specified within the DBMS_JAVA package.
SQL> call dbms_java.start_debugging('yourmachinename', 2286, 66);
There is no way to cause server-resident code to execute and break, that is, execute and remain indefinitely in a halted mode. Instead, when you start the DebugAgent, you must specify a timeout period for the DebugAgent to wait before terminating. The start call waits until the timeout expires or until the main thread is suspended and resumed before it completes. Calculate a timeout that includes enough time for your debugger to start up, but not so much as to delay your session if you cannot connect a debugger.
You can stop the debug agent explicitly through the stop_debugging method.
SQL> call dbms_java.stop_debugging();
Once a debug agent starts, it runs until you stop it, the debugger disconnects, or the session ends.
You can restart a stopped agent with any breakpoints still set with the restart_debugging method. The call waits until the timeout expires before it completes. You can also restart a running agent just to buy some seconds to suspend threads and set breakpoints.
SQL> call dbms_java.restart_debugging(66);
The DBMS_JAVA debug agent and proxy calls are published entry points to static methods that reside in oracle.aurora.debug.OracleAgent class. You can start, stop, and restart the debug agent in Java code using the class oracle.aurora.debug.OracleAgent directly through the following methods:
public static void start(String host, int port, long timeout_seconds); public static void stop(); public static void restart(long timeout_seconds);
Start jdb and attach it to the debug proxy using the password provided by the DebugProxy when the DebugAgent connected to it. In order to preserve your timeout, suspend all threads through jdb, set your breakpoints, and then resume.
Each time a debug agent connects to a debug proxy, the debug proxy starts a thread to wait for connections from a debugger. The thread prints out the number, name and address of the connecting agent, the port it is waiting on, and the port encoded as a password. Here, a specific port and password are provided for illustration only:
Agent Number: 1 Agent Name: servername Agent Address: eee.fff.jjj.kkk Agent Port: 2286 Agent Password: 3i65bn
You can then pass the password to a jdb-compatible debugger (JDK 1.1.6 or later):
jdb -password 3i65bn
The first thing you should do in the debugger is suspend all threads. Otherwise, your start_debugging call might time out and complete before you get your breakpoints set.
If your code writes to System.out or System.err, then you may also want to use the dbgtrace flag to jdb, which redirects these streams to the debugging console:
jdb -dbgtrace -password 3i65bn
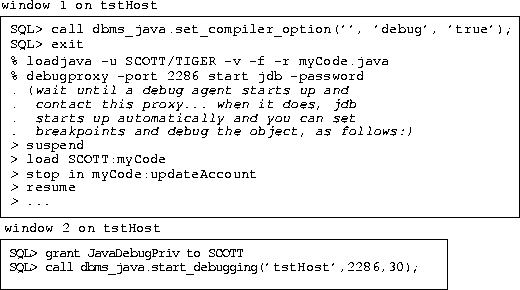
The following example shows how to debug an object that exists on the server. First, you need to start a proxy through the debugproxy command-line tool. This example starts up the proxy on the server, tstHost, and informs the debugproxy to start up the jdb debugger when contacted by the debug agent.
In another window, make sure that the debug agent user has the correct privileges and then start up the debug agent. Once the agent starts, the debugproxy starts up the jdb debugger and allows you to set your breakpoints. Since you have a specified amount of time before the agent times out, the first thing you should do is suspend all threads. Then, set all of your breakpoints before resuming. This suspends the timeout until you are ready to execute.
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|