Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A85397-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i SQL Reference Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A85397-01 |
|
SQL Statements:
ALTER CLUSTER to ALTER SYSTEM, 18 of 19
Use the ALTER SESSION statement to specify or modify any of the conditions or parameters that affect your connection to the database. The statement stays in effect until you disconnect from the database.
To enable and disable the SQL trace facility, you must have ALTER SESSION system privilege.
You do not need any privileges to perform the other operations of this statement unless otherwise indicated.
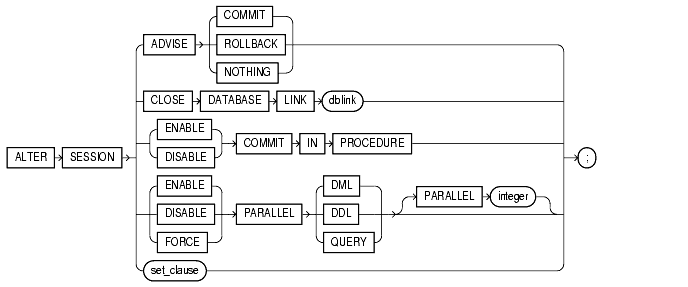
ADVISE
The ADVISE clause sends advice to a remote database to force a distributed transaction. The advice appears in the ADVICE column of the DBA_2PC_PENDING view on the remote database (the value 'C' for COMMIT, 'R' for ROLLBACK, and ' ' for NOTHING). If the transaction becomes in doubt, the administrator of that database can use this advice to decide whether to commit or roll back the transaction.
You can send different advice to different remote databases by issuing multiple ALTER SESSION statements with the ADVISE clause in a single transaction. Each such statement sends advice to the databases referenced in the following statements in the transaction until another such statement is issued.
|
See Also: Oracle8i Distributed Database Systems for more information on distributed transactions and how to decide whether to commit or roll back in-doubt distributed transactions |
CLOSE DATABASE LINK
Specify CLOSE DATABASE LINK to close the database link dblink. When you issue a statement that uses a database link, Oracle creates a session for you on the remote database using that link. The connection remains open until you end your local session or until the number of database links for your session exceeds the value of the initialization parameter OPEN_LINKS. If you want to reduce the network overhead associated with keeping the link open, use this clause to close the link explicitly if you do not plan to use it again in your session.
ENABLE | DISABLE COMMIT IN PROCEDURE
Procedures and stored functions written in PL/SQL can issue COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements. If your application would be disrupted by a COMMIT or ROLLBACK statement not issued directly by the application itself, use the DISABLE form of the COMMIT IN PROCEDURE clause to prevent procedures and stored functions called during your session from issuing these statements.
You can subsequently allow procedures and stored functions to issue COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements in your session by issuing the ENABLE form of this clause.
Some applications (such as SQL*Forms) automatically prohibit COMMIT and ROLLBACK statements in procedures and stored functions. Refer to your application documentation.
PARALLEL DML | DDL | QUERY
The PARALLEL parameter determines whether all subsequent DML, DDL, or query statements in the session will be considered for parallel execution. This clause enables you to override the degree of parallelism of tables during the current session without changing the tables themselves. Uncommitted transactions must either be committed or rolled back prior to executing this clause for DML.
The following types of DML operations are not parallelized regardless of this clause:
LONG or LOB datatypes.
See Also: Oracle8i Performance Guide and Reference for a detailed description of parallel DML features and hints
set_clause
Use the set_clause to set the session parameters that follow (parameters that are dynamic in the scope of the ALTER SESSION statement). You can set values for multiple parameters in the same set_clause.
|
Caution: Unless otherwise indicated, the parameters described here are initialization parameters, and the descriptions indicate only the general nature of the parameters. Before changing the values of initialization parameters, please refer to their full description in Oracle8i Reference or Oracle8i National Language Support Guide. |
CONSTRAINT[S] = {immediate | deferred | default }
The CONSTRAINT[S] parameter determines when conditions specified by a deferrable constraint are enforced. CONSTRAINT[S] is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter.
immediate indicates that the conditions specified by the deferrable constraint are checked immediately after each DML statement. This setting is equivalent to issuing the SET CONSTRAINTS ALL IMMEDIATE statement at the beginning of each transaction in your session.
deferred indicates that the conditions specified by the deferrable constraint are checked when the transaction is committed. This setting is equivalent to issuing the SET CONSTRAINTS ALL DEFERRED statement at the beginning of each transaction in your session.
default restores all constraints at the beginning of each transaction to their initial state of DEFERRED or IMMEDIATE.
CREATE_STORED_OUTLINES = { true | false| 'category_name' }
The CREATE_STORED_OUTLINES parameter determines whether Oracle should automatically create and store an outline for each query submitted during the session. CREATE_STORED_OUTLINES is not an initialization parameter.
true enables automatic outline creation for subsequent queries in the same session. These outlines receive a unique system-generated name and are stored in the DEFAULT category. If a particular query already has an outline defined for it in the DEFAULT category, that outline will remain and a new outline will not be created.
false disables automatic outline creation during the session. This is the default.
category_name has the same behavior as TRUE except that any outline created during the session is stored in the category_name category.
CURRENT_SCHEMA = schema
The CURRENT_SCHEMA parameter changes the current schema of the session to the specified schema. Subsequent unqualified references to schema objects during the session will resolve to objects in the specified schema. The setting persists for the duration of the session or until you issue another ALTER SESSION SET CURRENT_SCHEMA statement. CURRENT_SCHEMA is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter.
This setting offers a convenient way to perform operations on objects in a schema other than that of the current user without having to qualify the objects with the schema name. This setting changes the current schema, but it does not change the session user or the current user, nor does it give you any additional system or object privileges for the session.
|
See Also: Oracle8i Application Developer's Guide - Fundamentals for more information on this parameter |
CURSOR_SHARING = {force | exact}
The CURSOR_SHARING parameter determines what kind of SQL statements can share the same cursors.
exact causes only identical SQL statements to share a cursor.
force forces statements that may differ in some literals, but are otherwise identical, to share a cursor, unless the literals affect the meaning of the statement.
See Also: Oracle8i Performance Guide and Reference for information on setting this parameter in these and other environments
DB_BLOCK_CHECKING = {true | false}
The DB_BLOCK_CHECKING parameter controls whether data block checking is done. The default is false.
DB_FILE_MULTIBLOCK_READ_COUNT = integer
The DB_FILE_MULTIBLOCK_READ_COUNT parameter specifies with integer the maximum number of blocks read in one I/O operation during a sequential scan. The default is 8.
FAST_START_IO_TARGET = integer
The FAST_START_IO_TARGET parameter specifies the target number of I/Os (reads and writes) to and from buffer cache that Oracle should perform upon crash or instance recovery. Oracle continuously calculates the actual number of I/Os that would be needed for recovery and compares that number against the target. If the actual number is greater than the target, Oracle attempts to write additional dirty buffers to advance the checkpoint, while minimizing the affect on performance.
FLAGGER = { entry | intermediate | full | off }
The FLAGGER parameter specifies FIPS flagging, which causes an error message to be generated when a SQL statement issued is an extension of ANSI SQL92. FLAGGER is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter.
In Oracle, there is currently no difference between Entry, Intermediate, or Full level flagging. Once flagging is set in a session, a subsequent ALTER SESSION SET FLAGGER statement will work, but generates the message, ORA-00097. This allows FIPS flagging to be altered without disconnecting the session. off turns off flagging.
GLOBAL_NAMES = { true | false }
When you start an instance, Oracle determines whether to enforce global name resolution for remote objects accessed in SQL statements based on the value of the initialization parameter GLOBAL_NAMES. This parameter enables or disables global name resolution for the duration of the session. true enables the enforcement of global names. false disables the enforcement of global names. You can also enable or disable global name resolution for your instance with the GLOBAL_NAMES parameter of the ALTER SYSTEM statement.
Oracle recommends that you enable global name resolution if you use or plan to use distributed processing.
|
See Also: "Referring to Objects in Remote Databases" and Oracle8i Distributed Database Systems for more information on global name resolution and how Oracle enforces it |
HASH_AREA_SIZE = integer
The HASH_AREA_SIZE parameter specifies in bytes the amount of memory to use for hash join operations. The default is twice the value of the SORT_AREA_SIZE initialization parameter.
HASH_JOIN_ENABLED = {true | false}
The HASH_JOIN_ENABLED parameter enables or disables the use of the hash join operation in queries. The default is true, which enables hash joins.
HASH_MULTIBLOCK_IO_COUNT = integer
The HASH_MULTIBLOCK_IO_COUNT parameter specifies the number of data blocks to read and write during a hash join operation. The value multiplied by the DB_BLOCK_SIZE initialization parameter should not exceed 64 K. The default value for this parameter is 1. If the multi-threaded server is used, the value is always 1, and any value specified here is ignored.
INSTANCE = integer
The INSTANCE parameter in an Oracle Parallel Server environment accesses database files as if the session were connected to the instance specified by integer. INSTANCE is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter. For optimum performance, each instance of Oracle Parallel Server uses its own private rollback segments, freelist groups, and so on. In an Oracle Parallel Server environment, you normally connect to a particular instance and access data that is partitioned primarily for your use. If you must connect to another instance, the data partitioning can be lost. Setting this parameter lets you access an instance as if you were connected to your own instance.
ISOLATION_LEVEL = { SERIALIZABLE | READ COMMITTED }
The ISOLATION_LEVEL parameter specifies how transactions containing database modifications are handled. ISOLATION_LEVEL is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter.
SERIALIZABLE indicates that transactions in the session use the serializable transaction isolation mode as specified in SQL92. That is, if a serializable transaction attempts to execute a DML statement that updates rows currently being updated by another uncommitted transaction at the start of the serializable transaction, then the DML statement fails. A serializable transaction can see its own updates.
READ COMMITTED indicates that transactions in the session will use the default Oracle transaction behavior. Thus, if the transaction contains DML that requires row locks held by another transaction, then the DML statement will wait until the row locks are released.
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n = {null_string| {LOCATION=local_pathname| SERVICE=tnsnames_service}[MANDATORY | OPTIONAL] [REOPEN[=integer]]}
The LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter specifies up to five session-specific valid operating system pathnames or Oracle service names (plus other related options) as destinations for archive redo log file groups (n = integers 1 through 5).
Restrictions: If you set a value for this parameter, you cannot:
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST and LOG_ARCHIVE_DUPLEX_DEST in your initialization parameter file, nor can you set values for those parameters with the ALTER SYSTEM statement.
ALTER SYSTEM ARCHIVE LOG TO location statement.
See Also:
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter in Oracle8i Reference for detailed information on specifying pathnames
LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_STATE_n = {ENABLE | DEFER}
The LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_STATE_n parameter specifies the session-specific state associated with the corresponding LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter.
ENABLE specifies that any associated valid destination can be used for archiving. This is the default.
DEFER specifies that Oracle will not consider for archiving any destination associated with the corresponding LOG_ARCHIVE_DEST_n parameter.
LOG_ARCHIVE_MIN_SUCCEED_DEST = integer
The LOG_ARCHIVE_MIN_SUCCEED_DEST parameter specifies the session-specific minimum number of destinations that must succeed in order for the online log file to be available for reuse.
MAX_DUMP_FILE_SIZE = { size | UNLIMITED }
The MAX_DUMP_FILE_SIZE parameter specifies the upper limit of trace dump file size. Specify the maximum size as either a nonnegative integer that represents the number of blocks, or as UNLIMITED. If you specify UNLIMITED, no upper limit is imposed.
When you start an instance, Oracle establishes support based on the values of initialization parameters that begin with "NLS". You can query the dynamic performance table V$NLS_PARAMETERS to see the current NLS attributes for your session. For more information about NLS parameters, see Oracle8i National Language Support Guide.
NLS_CALENDAR = 'text'
The NLS_CALENDAR parameter explicitly specifies a new calendar type.
NLS_COMP = 'text'
The NLS_COMP parameter specifies that linguistic comparison is to be used according to the NLS_SORT parameter. This parameter obviates the need to specify NLS_SORT in SQL statements.
NLS_CURRENCY = 'text'
The NLS_CURRENCY parameter explicitly specifies a new value for the L number format element (the local currency symbol). The symbol cannot exceed 10 characters.
NLS_DATE_FORMAT = 'fmt'
The NLS_DATE_FORMAT parameter explicitly specifies a new default date format. The fmt value must be a valid date format model.
NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = language
The NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE parameter explicitly changes the language for names and abbreviations of days and months, and for spelled-out values of other date format elements.
NLS_DUAL_CURRENCY = 'text'
The NLS_DUAL_CURRENCY parameter explicitly specifies a new "Euro" (or other) dual currency symbol. The value of text is returned by the number format element U, and text cannot exceed 10 characters.
NLS_ISO_CURRENCY = territory
The NLS_ISO_CURRENCY parameter explicitly specifies the territory whose ISO currency symbol should be used. That territory's currency symbol then becomes the value of the C number format element.
NLS_LANGUAGE = language
The NLS_LANGUAGE parameter changes the language in which Oracle returns errors and other messages. This parameter also implicitly specifies new values for these items:
NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS = 'text'
The NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS parameter explicitly specifies a new decimal character and group separator. The text value must have this form:
'dg'
where: d is the new decimal character, and g is the new group separator.
The decimal character and the group separator must be two different single-byte characters, and cannot be a numeric value or any of the following characters: plus sign ("+"), minus sign or hyphen ("-" ), less-than sign ("<"), or greater-than sign (">").
If the decimal character is not a period (.), you must use single quotation marks to enclose all number values that appear in expressions in your SQL statements. When not using a period for the decimal point, use the TO_NUMBER function to ensure that a valid number is retrieved.
NLS_SORT = { sort | BINARY}
The NLS_SORT parameter changes the sequence into which Oracle sorts character values. sort specifies the name of a linguistic sort sequence. BINARY specifies a binary sort. The default is BINARY.
NLS_TERRITORY = territory
The NLS_TERRITORY parameter implicitly specifies new values for these items:
OBJECT_CACHE_MAX_SIZE_PERCENT = integer
The OBJECT_CACHE_MAX_SIZE_PERCENT parameter specifies the percentage of the optimal cache size that the session object cache can grow beyond the optimal size. The default is 10.
OBJECT_CACHE_OPTIMAL_SIZE = integer
The OBJECT_CACHE_OPTIMAL_SIZE parameter specifies (in kilobytes) the size to which the session object cache is reduced when it exceeds maximum size. The default is 100.
OPTIMIZER_INDEX_CACHING = integer
The OPTIMIZER_INDEX_CACHING parameter lets you tune the optimizer to favor nested loops joins and IN-list iterators. The value of integer indicates the percentage of the index blocks assumed to be in the cache.
OPTIMIZER_INDEX_COST_ADJ = integer
The OPTIMIZER_INDEX_COST_ADJ parameter lets you tune optimizer behavior for access path selection to make the optimizer more likely to select an index access path than a full table scan. The value of integer is a percentage indicating the importance the optimizer attaches to the index path compared with "normal". The default is 100 (indicating 100%), which makes the optimizer cost index access paths at the regular cost.
OPTIMIZER_MAX_PERMUTATIONS = integer
The OPTIMIZER_MAX_PERMUTATIONS parameter lets you limit the amount of work the optimizer expends on optimizing queries with large joins. The value of integer is the number of permutations of the tables the optimizer will consider with large joins.
OPTIMIZER_MODE = { all_rows | first_rows | rule | choose }
The OPTIMIZER_MODE parameter specifies the approach and mode of the optimizer for your session.
|
See Also: Oracle8i Concepts and Oracle8i Performance Guide and Reference for information on how to choose a goal for the cost-based approach based on the characteristics of your application |
all_rows specifies the cost-based approach and optimizes for best throughput.
first_rows specifies the cost-based approach and optimizes for best response time.
rule specifies the rule-based approach. (The rule-based optimizer does not use function-based indexes.)
choose causes the optimizer to choose an optimization approach based on the presence of statistics in the data dictionary.
OPTIMIZER_PERCENT_PARALLEL = integer
The OPTIMIZER_PERCENT_PARALLEL parameter specifies the amount of parallelism the optimizer uses in its cost functions. The default is 0 (no parallelism).
PARALLEL_BROADCAST_ENABLED = { true | false }
The PARALLEL_BROADCAST_ENABLED parameter lets you enhance performance during hash and merge joins.
PARALLEL_INSTANCE_GROUP = ' text '
The PARALLEL_INSTANCE_GROUP parameter identifies the parallel instance group to be used for spawning parallel query slaves. The default is all active instances.
PARALLEL_MIN_PERCENT = integer
The PARALLEL_MIN_PERCENT parameter specifies the minimum percent of threads required for parallel query. The default is 0 (no parallelism).
PARTITION_VIEW_ENABLED = { true | false }
The PARTITION_VIEW_ENABLED parameter, when set to true, causes the optimizer to skip unnecessary table accesses in a partition view.
PLSQL_V2_COMPATIBILITY = { true | false }
The PLSQL_V2_COMPATIBILITY parameter, if true, modifies the compile-time behavior of PL/SQL programs to allow language constructs that are illegal in Oracle8 and Oracle8i (PL/SQL V3), but were legal in Oracle7 (PL/SQL V2). false disallows illegal Oracle7 PL/SQL V2 constructs. This is the default.
|
See Also: PL/SQL User's Guide and Reference and Oracle8i Reference for more information about this session parameter |
QUERY_REWRITE_ENABLED = { true | false }
The QUERY_REWRITE_ENABLED parameter enables or disables query rewrite on all materialized views that have not been explicitly disabled. Query rewrite is disabled by default. It is also disabled by rule-based optimization (that is, if the OPTIMIZER_MODE parameter is set to rule).
This parameter has the following additional effect on the use of function-based indexes:
true: Oracle will use function-based indexes to derive values of SQL expressions. If in addition the QUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITY parameter is set to any value other than enforced, Oracle will derive such values even if the index is based on a user-defined (rather than SQL) function.
false: Oracle will not use function-based indexes to derive values of SQL expressions, but it will use such indexes to obtain values of real columns in the index.
Enabling or disabling query rewrite does not affect descending indexes.
A setting of true has no effect on materialized views that cannot be created with the ENABLE QUERY REWRITE clause, such as materialized views created totally or in part from a view.
QUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITY
QUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITY ={ enforced | trusted | stale_tolerated }
The QUERY_REWRITE_INTEGRITY parameter sets the minimum consistency level for query rewrite. The following values are permitted:
enforced is the safest level. It relies only on system-enforced relationships so that data integrity and correctness can be guaranteed. This level ensures that query rewrite will not use any function-based index or any materialized view that includes a call to a user-defined function.
In addition, this level ensures that query rewrite will not use any dimensional information or any constraints enabled with the RELY keyword.
trusted specifies that materialized views created with the ON PREBUILT TABLE clause are supported, and trusted but unenforced join relationships are accepted. Query rewrite uses join information from dimensions and enables unenforced constraints with the RELY keyword.
stale_tolerated specifies that any stale, usable materialized view may be used.
This parameter does not affect descending indexes.
|
See Also:
|
REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE = { timestamp | signature }
The REMOTE_DEPENDENCIES_MODE specifies how dependencies of remote stored procedures are handled by the session.
SESSION_CACHED_CURSORS = integer
The SESSION_CACHED_CURSORS parameter specifies the number of frequently used cursors that can be retained in the cache. The cursors can be open or closed, which is particularly useful for Oracle tools that close all session cursors associated with a form when switching to another form. In such cases, frequently used cursors do not have to be reparsed. A least recently used algorithm ages out entries in the cache to make room for new entries when needed.
SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES = { true | false }
The SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES parameter controls the use and reporting of tables with unusable indexes or index partitions. SKIP_UNUSABLE_INDEXES is a session parameter only, not an initialization parameter.
true disables error reporting of indexes and index partitions marked UNUSABLE. Allows all operations (inserts, deletes, updates, and selects) to tables with unusable indexes or index partitions.
false enables error reporting of indexes marked UNUSABLE. Does not allow inserts, deletes, and updates to tables with unusable indexes or index partitions. This is the default.
SORT_AREA_RETAINED_SIZE = integer
The SORT_AREA_RETAINED_SIZE parameter specifies (in bytes) the maximum amount of memory that each sort operation will retain after the first fetch is done, until the cursor ends. If you do not explicitly set this parameter in the initialization parameter file or dynamically, Oracle uses the value of the SORT_AREA_SIZE parameter.
SORT_AREA_SIZE = integer
The SORT_AREA_SIZE parameter specifies (in bytes) the maximum amount of memory to use for each sort operation. The default is OS-dependent.
SORT_MULTIBLOCK_READ_COUNT = integer
The SORT_MULTIBLOCK_READ_COUNT parameter specifies the number of database blocks to read each time a sort performs a read from temporary segments. The default is 2.
SQL_TRACE = { true | false }
The SQL trace facility generates performance statistics for the processing of SQL statements. When you begin a session, Oracle enables or disables the SQL trace facility based on the value of this parameter. You can subsequently enable or disable the SQL trace facility for your own session with the SQL_TRACE parameter of the ALTER SESSION statement.
SQL_TRACE is an initialization parameter. However, when you change its value with an ALTER SESSION statement, the results are not reflected in the V$PARAMETER view. Therefore, in this context it is considered a session parameter only.
|
See Also: Oracle8i Performance Guide and Reference for more information on the SQL trace facility, including how to format and interpret its output |
STAR_TRANSFORMATION_ENABLED = { true | false }
The STAR_TRANSFORMATION_ENABLED parameter determines whether a cost-based query transformation will be applied to star queries. The default is false.
TIMED_STATISTICS = {true | false }
The TIMED_STATISTICS parameter specifies whether the server requests the time from the operating system when generating time-related statistics. The default is false.
USE_STORED_OUTLINES = { true | false | 'category_name' }
The USE_STORED_OUTLINES parameter determines whether the optimizer will use stored outlines to generate execution plans. USE_STORED_OUTLINES is not an initialization parameter.
true causes the optimizer to use outlines stored in the DEFAULT category when compiling requests.
false specifies that the optimizer should not use stored outlines. This is the default.
category_name causes the optimizer to use outlines stored in the category_name category when compiling requests.
Issue the following statement to enable parallel DML mode for the current session:
ALTER SESSION ENABLE PARALLEL DML;
The following transaction inserts an employee record into the emp table on the database identified by the database link site1 and deletes an employee record from the emp table on the database identified by site2:
ALTER SESSION ADVISE COMMIT; INSERT INTO emp@site1 VALUES (8002, 'FERNANDEZ', 'ANALYST', 7566, TO_DATE('04-OCT-1992', 'DD-MON-YYYY'), 3000, NULL, 20); ALTER SESSION ADVISE ROLLBACK; DELETE FROM emp@site2 WHERE empno = 8002; COMMIT;
This transaction has two ALTER SESSION statements with the ADVISE clause. If the transaction becomes in doubt, site1 is sent the advice 'COMMIT' by virtue of the first ALTER SESSION statement and site2 is sent the advice 'ROLLBACK' by virtue of the second.
This statement updates the employee table on the sales database using a database link, commits the transaction, and explicitly closes the database link:
UPDATE emp@sales SET sal = sal + 200 WHERE empno = 9001; COMMIT; ALTER SESSION CLOSE DATABASE LINK sales;
The following statement dynamically changes the default date format for your session to 'YYYY MM DD-HH24:MI:SS':
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_DATE_FORMAT = 'YYYY MM DD HH24:MI:SS';
Oracle uses the new default date format:
SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE) Today FROM DUAL; TODAY ------------------- 1997 08 12 14:25:56
The following statement changes the language for date format elements to French:
ALTER SESSIONSET NLS_DATE_LANGUAGE = French;SELECT TO_CHAR(SYSDATE, 'Day DD Month YYYY') TodayFROM DUAL;TODAY---------------------------Mardi 28 Février 1997
The following statement dynamically changes the ISO currency symbol to the ISO currency symbol for the territory America:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_ISO_CURRENCY = America; SELECT TO_CHAR( SUM(sal), 'C999G999D99') Total FROM emp; TOTAL ------------- USD29,025.00
The following statement dynamically changes the decimal character to comma (,) and the group separator to period (.):
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_NUMERIC_CHARACTERS = ',.' ;
Oracle returns these new characters when you use their number format elements:
SELECT TO_CHAR( SUM(sal), 'L999G999D99') Total FROM emp ; TOTAL ------------- FF29.025,00
The following statement dynamically changes the local currency symbol to 'DM':
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_CURRENCY = 'DM'; SELECT TO_CHAR( SUM(sal), 'L999G999D99') Total FROM emp; TOTAL ------------- DM29.025,00
The following statement dynamically changes to French the language in which error messages are displayed:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_LANGUAGE = FRENCH; SELECT * FROM DMP; ORA-00942: Table ou vue inexistante
The following statement dynamically changes the linguistic sort sequence to Spanish:
ALTER SESSION SET NLS_SORT = XSpanish;
Oracle sorts character values based on their position in the Spanish linguistic sort sequence.
To enable the SQL trace facility for your session, issue the following statement:
ALTER SESSION SET SQL_TRACE = TRUE;
This statement enables query rewrite in the current session for all materialized views that have not been explicitly disabled:
ALTER SESSION SET QUERY_REWRITE_ENABLED = TRUE;
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|