Release 3 (8.1.7)
Part Number A86632-01
Library |
Product |
Contents |
Index |
| Oracle8i Migration Release 3 (8.1.7) Part Number A86632-01 |
|
This chapter includes definitions for words used throughout this manual and information about changing the word-size of your database. This chapter also provides information about running different versions and releases of Oracle on the same computer system. In addition, this chapter covers other topics that relate to migration, upgrading, and downgrading operations.
Specifically, this chapter covers the following topics:
The following terms (specified in italic) are used throughout this document:
The instructions in this document describe moving between different versions and releases of Oracle. Figure 1-1 describes what each part of a release number represents.
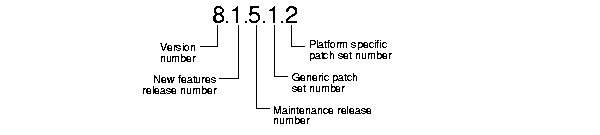
When a statement is made in this book about a version of Oracle, the statement applies to all releases in that version. References to version 8 include all releases in release 8.0 and release 8.1; references to Oracle7 include all version 7 releases, including release 7.0, 7.1, 7.2, and 7.3.
Similarly, when a statement is made in this book about a maintenance release, the statement applies to all production patch releases and port specific patch releases within that maintenance release. So, a statement about release 8.0 applies to all production releases within release 8.0, including release 8.0.3, 8.0.4, 8.0.5, and 8.0.6, but not necessarily to release 8.0.2, because that release was a beta release.
The same logic applies to patch releases. When a statement is made in this book about a patch release, the statement applies to all port-specific patch releases within that patch release. So, a statement about release 8.1.5 applies to release 8.1.5.0, 8.1.5.1, and all other port-specific patch releases within release 8.1.5.
Migration is the process of transforming an installed version of an Oracle database into a later version. For example, transforming an Oracle7 database into an Oracle8i database is migrating the database.
Upgrading is the process of transforming an Oracle database from an installed release into a later release of the same version. For example, transforming patch release 8.0.3 into patch release 8.0.4 is upgrading, and transforming an 8.0 maintenance release into an 8.1 maintenance release is upgrading.
|
See Also:
Chapter 7, "Upgrading from a Previous Version 8 Release to the New Oracle8i Release" for information about upgrading. |
Downgrading is the process of transforming an installed version of an Oracle database from a later release back into an earlier release. For example, transforming an Oracle database from release 8.1.5 back into release 8.0.5 is downgrading, and transforming an Oracle database from Oracle8i back into Oracle7 is downgrading.
|
See Also:
Chapter 13, "Downgrading to an Older Version 8 Release" for information about downgrading a release 8.1 database to an earlier 8.1 release or to an 8.0 release. See Chapter 14, "Downgrading to Oracle7" for information about downgrading to Oracle7. |
The source database is the database to be migrated to Oracle8i; during migration, the source database uses an older version of Oracle software, such as version 6 or Oracle7. The target database is the database into which you are migrating the source database; during migration, the target database uses new Oracle8i software.
You can run different versions of Oracle on the same computer system at the same time. However, each version can only access a database that is consistent with its version. For example, if you have version 7 and version 8 installed on the same computer system, then the version 7 server can access version 7 databases but not version 8 databases, and the version 8 server can access version 8 databases but not version 7 databases. For following sections provide general information about running multiple versions and releases of Oracle.
|
Caution: It is not possible to install release 8.1 products into an existing release 8.0 or version 7 Oracle home. This functionality was only available for certain previous releases and has not been continued. An Oracle 8.1 and release must be installed in an Oracle home that is separate from previous releases of Oracle. Also, you cannot have more than one release per Oracle home. Oracle Corporation recommends that you adopt an Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) when creating multiple Oracle homes. "Using Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA)" for more information. |
You can install version 7 and version 8 databases in multiple (separate) Oracle homes and have both version 7 and version 8 clients connecting to version 7 and version 8 databases. Figure 1-2 shows an example of this network configuration:
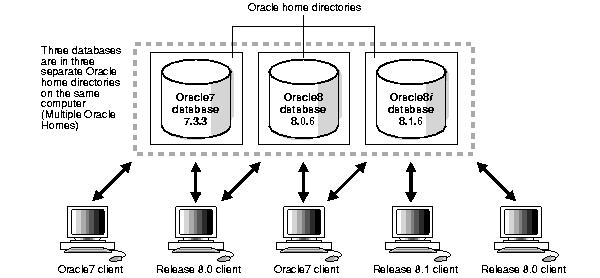
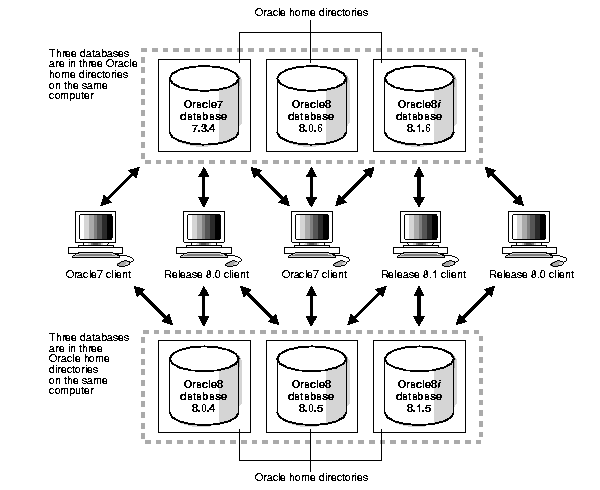
You can install version 7 and version 8 databases on separate computers and have both version 7 and version 8 clients connecting to both databases. The figure below shows two computers and a number of version 7 and version 8 clients.
Figure 1-3 illustrates this network configuration:
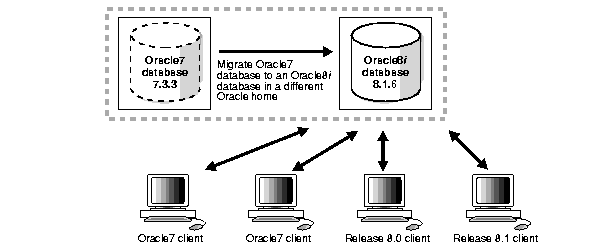
You can migrate your version 7 database to a version 8 database and have both version 7 and version 8 clients connecting to the version 8 database. You cannot migrate your version 7 database to a version 8 database in the same Oracle home.
Figure 1-4 illustrates this network configuration:
You can upgrade your release 8.0 database, for example release 8.0.6, to release 8.1 and have both version 7 and release 8.0 clients connecting to the release 8.1 database. You cannot upgrade your release 8.0 database to a release 8.1 database in the same Oracle home.
Figure 1-5 illustrates this network configuration:
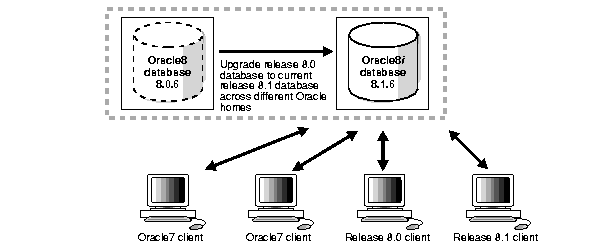
You can upgrade a previous release 8.1 database, for example release 8.1.5, to the current 8.1 release and have version 7, release 8.0, and release 8.1 clients connecting to the release 8.1 database. You can upgrade your previous release 8.1 database to the current release 8.1 database in the same Oracle home, but doing so is not recommended. Oracle Corporation recommends using a separate Oracle home directory for the new 8.1 release.
Figure 1-6 illustrates this network configuration:
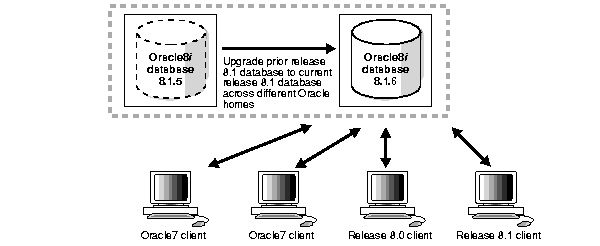
You can migrate some or all of your version 7 clients to release 8.1. You can also migrate your version 7 database to a release 8.1 database or upgrade your release 8.0 database to the current release 8.1 database at a later date.
Figure 1-7 illustrates this network configuration:
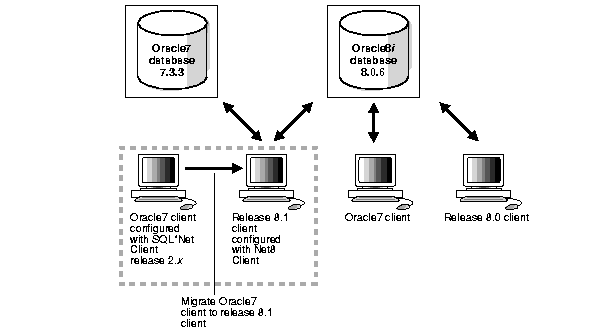
Whether you are migrating a version 7 database or upgrading a version 8 database, Oracle Corporation recommends the Optimal Flexible Architecture (OFA) standard for your Oracle8i installations. The OFA standard is a set of configuration guidelines for efficient and reliable Oracle databases that require little maintenance.
OFA provides the following benefits:
If you are not using the OFA standard currently, then switching to the OFA standard involves modifying your directory structure and relocating your database files.
|
See Also:
Your Oracle operating-system specific documentation for more information about OFA, and the Oracle8i Administrator's Guide for information about relocating your database files. |
You need to run various scripts when you perform migration, upgrade, and downgrade operations. When you run a script, the script may report "ORA-" errors. In general, you should look for errors that alert you to insufficient space, and for errors that alert you that a script failed to run. If you see these types of errors, then the operation may not be completely successful. However, you typically can ignore errors about the failure to alter or drop an object that does not exist.
You can change the word-size of your Oracle database server during a migration, upgrade, or downgrade operation. A change in word-size includes the following scenarios:
If you are changing word-size during a migration, upgrade, or downgrade operation, then no additional action is required. The word-size is changed automatically during any of these operations. However, if you want to change the word-size within the same release, then follow the instructions in "Changing the Word-Size of Your Current Release". For example, if you have the 32-bit version of Oracle release 8.1.7 and you want to switch to the 64-bit version of Oracle release 8.1.7, then you must complete this procedure.
The following information applies if you are upgrading or downgrading your hardware from 32-bit to 64-bit or from 64-bit to 32-bit:
The on-disk format for database data, redo, and undo is identical for the 32-bit and 64-bit installations of Oracle. The only internal structural differences between the 32-bit and 64-bit Oracle installations are the following:
Rolling upgrades are not supported. A rolling upgrade is one in which different instances of the same database in Oracle Parallel Server are upgraded to a new version or release of Oracle one at a time. Therefore, a rolling upgrade would result in different releases running concurrently during the upgrade process. If you are using Oracle Parallel Server, then you must upgrade all instances at the same time.
If you want to deinstall old options when you migrate or upgrade to a new release of Oracle, then use the installer to deinstall them. You can deinstall them before or after you upgrade or migrate, but you must use the version of the installer that corresponds with the items you want to remove.
For example, if you are running release 8.0 of Oracle with Oracle Parallel Server installed, and you decide that you do not need this option when you upgrade to release 8.1, then you should deinstall Oracle Parallel Server in one of the following ways:
|
|
 Copyright © 1996-2000, Oracle Corporation. All Rights Reserved. |
|